111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

AZD4547 可通过抑制炎症减轻脂多糖诱导的急性肾脏损伤:FGFR1 在肾小管上皮细胞中的作用
Authors Chen X, Zhang X, Xu J, Zhao Y, Bao J, Zheng Z, Han J
Received 23 July 2019
Accepted for publication 16 February 2020
Published 26 February 2020 Volume 2020:14 Pages 833—844
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S224343
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sukesh Voruganti
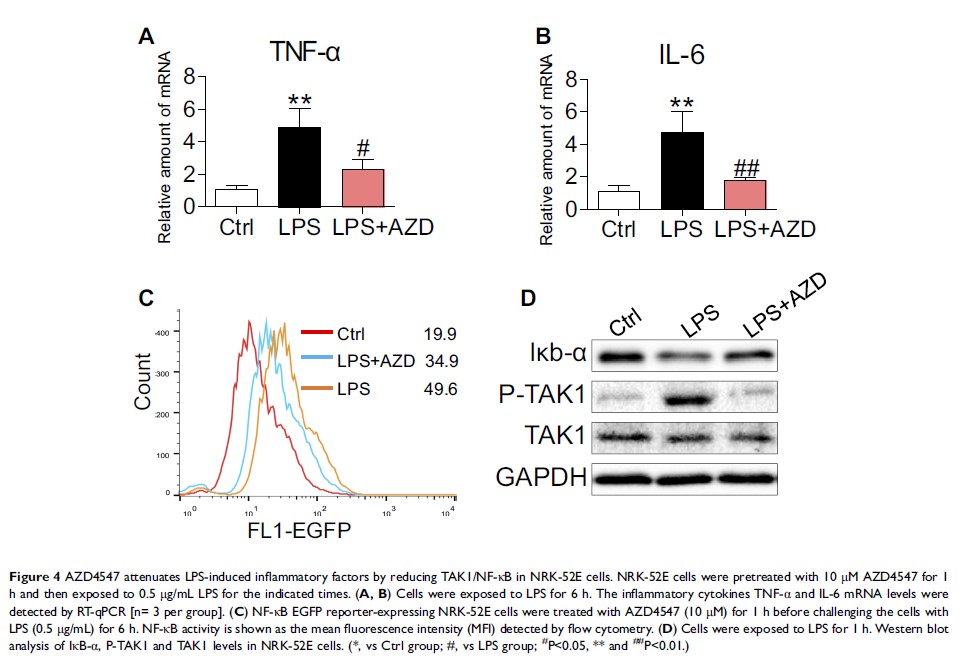
Introduction: Inflammation plays an important role in the pathogenesis of acute kidney injury (AKI). Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 (FGFR1) signaling is implicated in kidney pathology. AZD4547 is a small molecule inhibitor of FGFR1.
Materials and Methods: Here, we investigated whether AZD4547 could mitigate inflammatory responses in AKI. C57BL/6 mice were injected with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) to induce AKI. FGFR1 was blocked using AZD4547 or CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing. After immunofluorescent double-staining of kidney tissues showing that P-FGFR1 was localized to renal tubular epithelial cells, a tubular epithelial cell line (NRK-52E) was used for in vitro analysis.
Results: AZD4547 significantly reduced renal inflammation, cell apoptosis, and kidney dysfunction in AKI mice. In vitro, treatment of NRK-52E cells with AZD4547 attenuated LPS-induced inflammatory responses and was associated with downregulated P-FGFR1 levels. These findings were further confirmed in NRK-52E cells by knocking down the expression of FGFR1.
Conclusion: Our findings provide direct evidence that FGFR1 mediates LPS-induced inflammation leading to renal dysfunction. We also show that AZD4547 is a potential therapeutic agent to reduce inflammatory responses in AKI. Both FGFR1 and AZD4547 may interesting therapeutic options to combat AKI.
Keywords: acute kidney injury, lipopolysaccharide, inflammation, AZD4547, renal tubular epithelial cells