111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

姜黄素对颈动脉内膜切除术后动脉再狭窄的抑制作用及其体内外相关机制
Authors Zhang D, Yang Y, Li Y, Zhang G, Cheng Z
Received 2 September 2019
Accepted for publication 10 February 2020
Published 26 February 2020 Volume 2020:14 Pages 855—866
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S229607
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yan Zhu
Objective: The present study aimed to assess the effect of curcumin (Cur) on carotid artery restenosis following carotid endarterectomy (CEA) and its associated mechanism in vivo and in vitro.
Methods: Ang II was used to induce excessive proliferation of rabbit aortic smooth muscle cells (CCC-SMC-1) in order to establish a hemadostenosis cell model. Similarly, the animal model of carotid artery restenosis was established by carotid artery gas drying injury combined with high-fat feed prior to CEA. CCC-SMC-1 cells and animals were treated by Cur and its effects on neointimal hyperplasia, inflammation and oxidative stress were detected and observed. The proteins that were associated with the Raf/MEK/ERK pathway were detected in cells and rabbit carotid artery tissues.
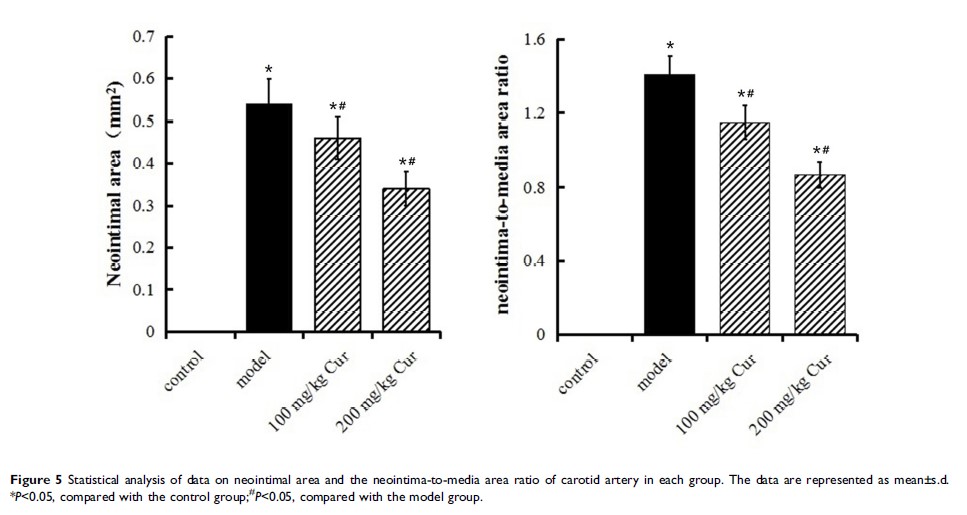
Results: Cur inhibited the proliferation of smooth muscle cells and neointimal formation and reduced the inflammation and oxidative stress indices. Concomitantly, Cur reduced the phosphorylation of the Raf/MEK/ERK pathway proteins.
Conclusion: Cur could inhibit carotid restenosis following CEA by inhibiting the activation of the Raf/MEK/ERK pathway.
Keywords: curcumin, carotid endarterectomy, restenosis, vascular smooth muscle cells, Raf/MEK/ERK