111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

葡糖酸激酶 IDNK 促进肝癌细胞增殖并抑制其凋亡
Authors Wu XM, Jin C, Gu YL, Chen WQ, Zhu MQ, Zhang S, Zhang Z
Received 10 October 2019
Accepted for publication 13 February 2020
Published 26 February 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 1767—1776
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S234055
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Arseniy Yuzhalin
Purpose: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the deadliest cancers globally with a poor prognosis. Breakthroughs in the treatment of HCC are urgently needed. This study explored the role of IDNK in the development and progression of HCC.
Methods: IDNK expression was suppressed using short hairpin (shRNA) in BEL-7404 and Huh-7 cells. The expression of IDNK in HCC cells after IDNK knockdown was evaluated by real-time quantitative RT-PCR analysis and Western blot. After IDNK silencing, the proliferation and apoptosis of HCC cells were evaluated by Celigo cell counting, flow cytometry analysis, MTT assay, and caspase3/7 assay. Gene expressions in BEL-7404 cells transfected with IDNK shRNA lentivirus plasmid and blank control plasmid were evaluated by microarray analysis. The differentially expressed genes induced by deregulation of IDNK were identified, followed by pathway analysis.
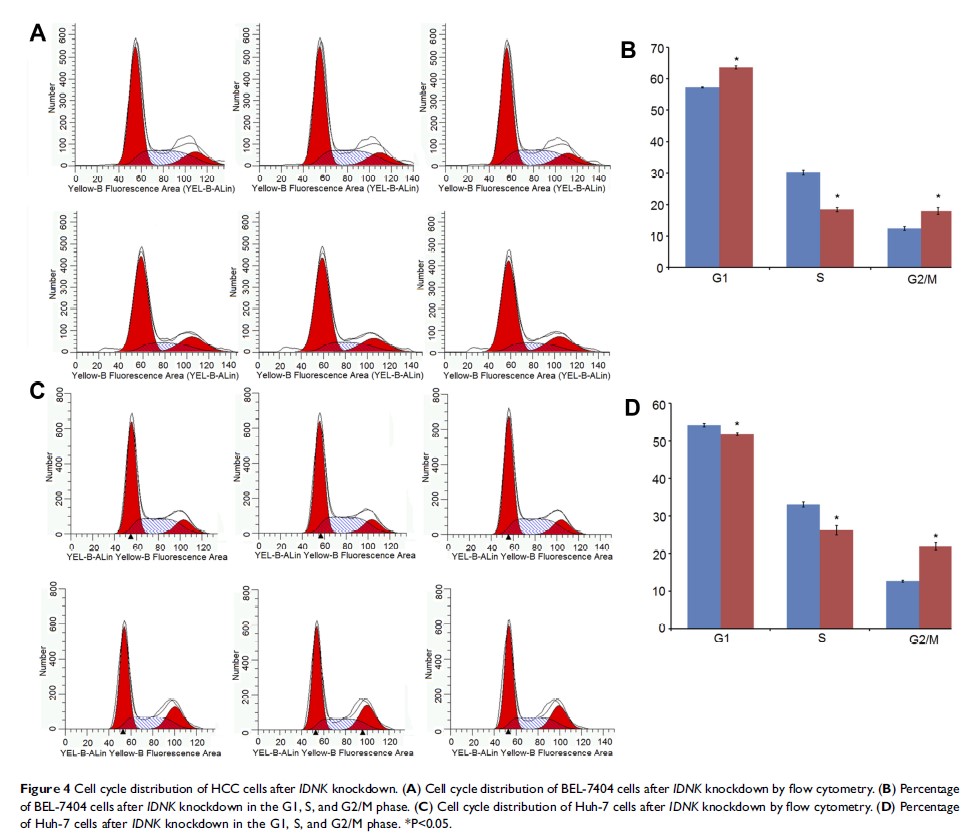
Results: The expression of IDNK at the mRNA and protein levels was considerably reduced in shRNA IDNK transfected cells. Knockdown of IDNK significantly inhibited HCC cell proliferation and increased cell apoptosis. A total of 1196 genes (585 upregulated and 611 downregulated) were differentially expressed in IDNK knockdown BEL-7404 cells. The pathway of tRNA charging with Z-score = − 3 was significantly inhibited in BEL-7404 cells with IDNK knockdown.
Conclusion: IDNK plays a key role in the proliferation and apoptosis of HCC cells. IDNK may be a candidate therapeutic target for HCC.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma cells, shRNA IDNK, cell proliferation, cell apoptosis, microarray, differentially expressed gene