111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

姜黄素通过阻止 Tafazzin/Yes 相关蛋白轴来抑制乳腺癌的肿瘤发生
Authors Shen Y, Han Z, Liu S, Jiao Y, Li Y, Yuan H
Received 20 January 2020
Accepted for publication 14 February 2020
Published 27 February 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 1493—1502
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S246691
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Bilikere Dwarakanath
Purpose: This study was aimed to explore the anti-tumor effect of curcumin on breast cancer (BC) and the underlying mechanism involving Tafazzin (TAZ)/Yes-associated protein (YAP) axis.
Methods: Different concentrations of curcumin (0, 10, 20 and 30 μM) were used to treat BC cells (MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 cells). The viability, colony formation, apoptosis, migration, and invasion of BC cells were detected by MTT, colony formation, flow cytometry, wound-healing and transwell assay, respectively. The protein expression of TAZ and YAP (effectors of Hippo signaling pathway) was detected by Western blot. MDA-MB-231 cells were injected into mice to verify the anti-tumor effect of curcumin in vivo.
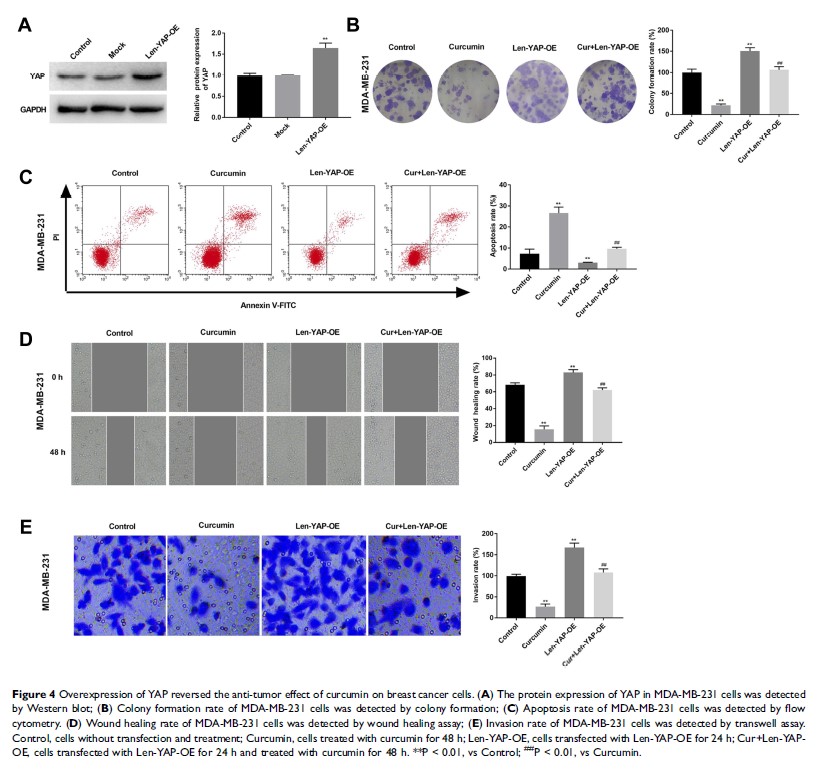
Results: Curcumin (20 and 30 μM) inhibited the proliferation, migration and invasion, and promoted the apoptosis of MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 cells. Curcumin decreased the protein expression of TAZ and YAP in MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 cells. Overexpression of YAP reversed the anti-tumor effect of curcumin on MDA-MB-231 cells. In addition, curcumin (100, 200 and 300 mg/kg/d) inhibited the growth of tumor xenografts in mice, and down-regulated the protein expression of TAZ and YAP in tumor xenografts. However, curcumin at a concentration of 300 mg/kg/d slowed the increasing of body weight in mice.
Conclusion: Curcumin inhibited the tumorigenesis of BC by blocking TAZ/YAP axis.
Keywords: curcumin, breast cancer, Hippo signaling pathway, proliferation, metastasis