111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

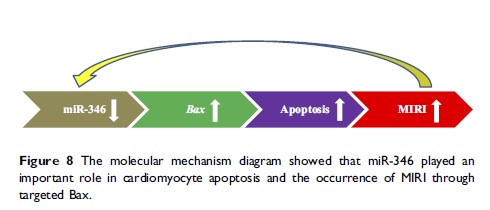
miR-346 通过靶向大鼠 Bax 抑制心肌缺血再灌注损伤的细胞凋亡
Authors Lv X, Lu P, Hu Y, Xu T
Received 8 January 2020
Accepted for publication 19 February 2020
Published 27 February 2020 Volume 2020:14 Pages 895—905
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S245193
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Jianbo Sun
Purpose: Myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury (MIRI) is a common pathophysiological process after occlusion of the blood vessels to restore blood supply. Apoptosis is one of the ways of myocardial cell death in this process. MicroRNAs (miRNAs), a class of short and noncoding RNAs, are involved in multiple biological processes by post-transcriptionally targeting their downstream effectors. To date, whether miRNAs exert biological effects in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) injury remains to be further studied.
Methods: In this study, we induced MIRI model by ligating rat left anterior descending artery (LAD) for 30 mins and reperfusion for 2 hrs. The differential expression profile of miRNAs in rat models of MIRI was analyzed by miRNAs sequencing.
Results: We found that miRNAs sequencing analysis showed the expressions of 15 types of miRNAs, including miR-346, were downregulated and 29 types of miRNAs were elevated in the MIRI rat model. We observed the key regulator of apoptosis Bax was a predicted downstream target of miR-346 using online software TargetScan. And luciferase reporter assay was utilized to certify this prediction. Over-expression of miR-346 can attenuate myocardial injury and narrow infarct area by inhibiting myocardial cell apoptosis in rat models.
Conclusion: This study revealed a novel pathway, miR-346/Bax axis, in the regulation of apoptosis in MIRI and which might be a new molecular mechanism and therapeutic target.
Keywords: miR-346, myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury, apoptosis, Bax