111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

中药在肿瘤相关巨噬细胞中的肿瘤靶向作用及分子机制
Authors He J, Yin P, Xu K
Received 18 July 2019
Accepted for publication 5 February 2020
Published 28 February 2020 Volume 2020:14 Pages 907—919
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S223646
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sukesh Voruganti
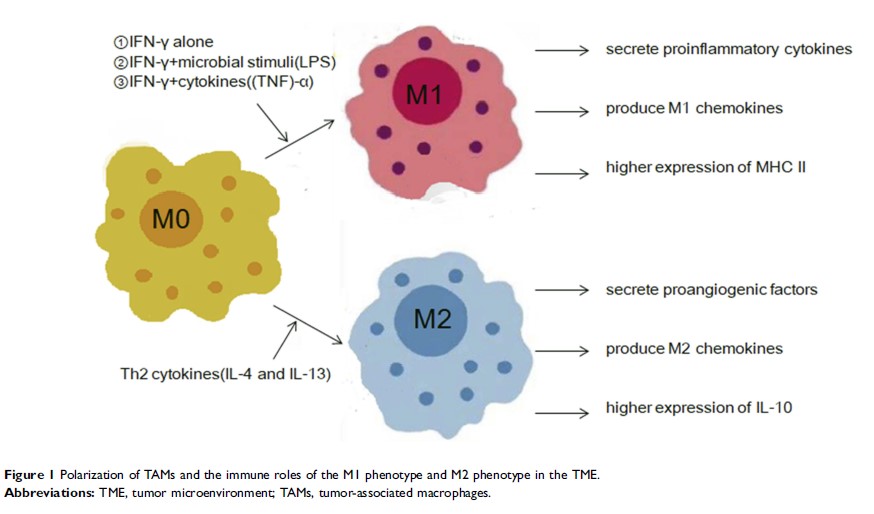
Abstract: Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) has been used as a significant cancer treatment method for many years in China. It has been demonstrated that TCM could assist in inhibiting the growth of tumors and prolonging the survival rates of cancer patients. Although the mechanism of TCM are still not clear, accumulating evidence has shown that they may be related to the tumor microenvironment (TME). Tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) play a significant role in TME and are polarized to two phenotypes, M1 (classically activated) and M2 (alternatively activated) TAMs. The two different phenotypes of TAMs play converse roles in the TME and M2-polarized tumor-associated macrophages (M2-TAMs) always lead to poor prognosis in cancer patients compared to M1-polarized tumor-associated macrophages (M1-TAMs). In this review, the potential correlation between TCM and TAMs (especially the M2 phenotype) in tumor progression and promising TCM strategies targeting TAMs in cancer are discussed.
Keywords: traditional Chinese medicine, TCM, tumor-associated macrophages, TAMs, tumor microenvironment