111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

血清 CC16 浓度降低与慢性阻塞性肺疾病的严重程度有关,并有助于疾病的诊断和评估
Authors Rong B, Fu T, Gao W, Li M, Rong C, Liu W, Liu H
Received 9 September 2019
Accepted for publication 13 January 2020
Published 2 March 2020 Volume 2020:15 Pages 461—470
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/COPD.S230323
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Chunxue Bai
Background: The aim of this study was to reveal the correlations between serum concentration of Clara cell secretory protein (CC16) and clinical parameters of stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Patients and Methods: Serum concentration of CC16 was determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The correlations between serum concentration of CC16 and clinical parameters was performed by linear correlation analysis and multiple linear regression analysis. The sensitivity and specificity of serum CC16 for differential diagnosis of COPD were determined by receiver operator characteristic curve (ROC).
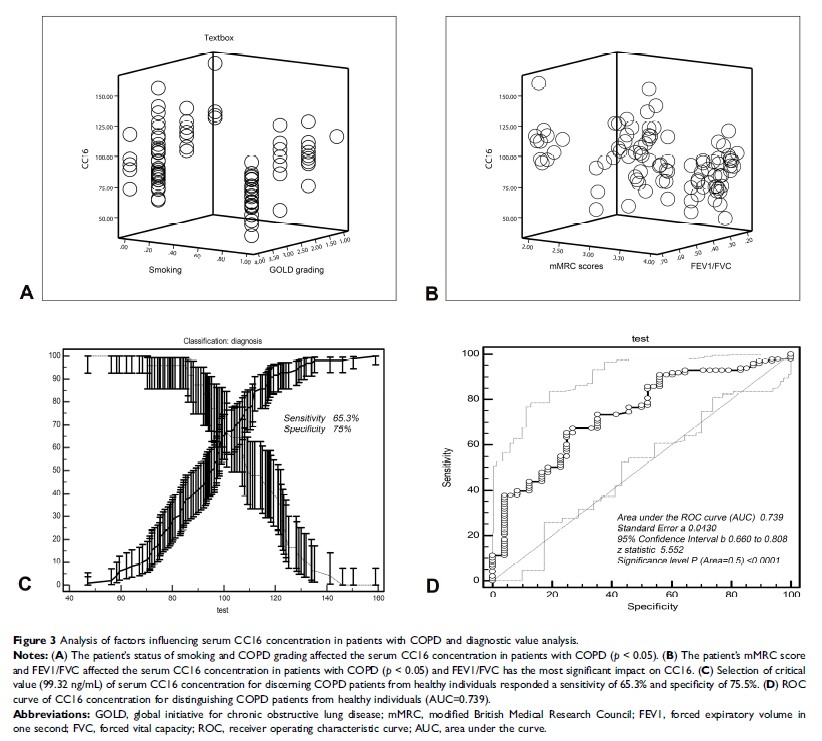
Results: The serum concentration of CC16 was down-regulated in stable COPD patients compared with healthy control group (p < 0.05). The decreased serum CC16 was negatively related to smoking (p < 0.05), GOLD grading (p < 0.005), mMRC score (p < 0.05) and medical history (p < 0.05) of patients, but positively correlated with pulmonary function (p < 0.05). The smoking, FEV1/FVC values, COPD grading and mMRC scores all affected the concentration of CC16 (p < 0.05). The decreased CC16 was an independent risk factor in the process of deterioration of lung function. The sensitivity and specificity of serum CC16 for identifying COPD reached to 65.3% and 75%.
Conclusion: Decreased serum concentration of CC16 correlated with the disease progression of COPD, suggesting that it can be used as an indicator contributing to the diagnosis and assessment of COPD.
Keywords: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, COPD, Clara cell secretory protein 16, CC16