111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

老年患者侵袭性真菌病的流行病学和死亡率相关因素:来自中国南方的 20 年回顾性研究
Authors Gong Y, Li C, Wang C, Li J, Ding M, Chen D, Lao M
Received 12 December 2019
Accepted for publication 19 February 2020
Published 3 March 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 711—723
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IDR.S242187
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Joachim Wink
Introduction: Invasive fungal disease (IFD) is a life-threatening infection. The epidemiology and clinical features of IFD in the elderly population are less discussed. The aim of this study was to explore the epidemiology and mortality-associated factors for IFD in the elderly inpatients.
Methods: A retrospective study enrolling 512 elderly inpatients from The First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University during the last two decades was performed.
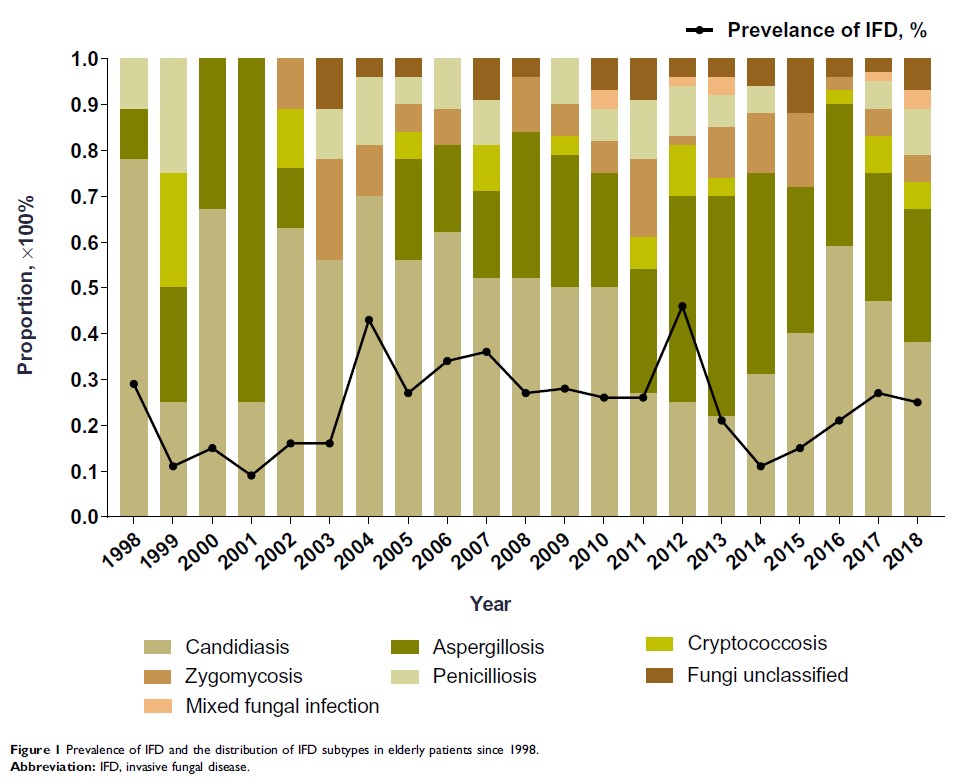
Results: The annual prevalence of IFD was 0.1– 0.5%. Candidiasis was the most common (236/521, 45.3%). An increasing trend was observed in aspergillosis from 11.1% in year 1998 to 28.8% in year 2018. The common infective sites of candidiasis were abdominal cavity (83/236, 35.2%) and bloodstream (55/236, 23.3%). Invasive aspergillosis mainly developed in the sinus (74/149, 49.7%) and lung (65/149, 43.6%). Patients with diabetes mellitus (DM) (59/126, 46.8%), solid organ malignancy (84/114, 73.7%), chronic kidney disease (CKD) (40/62, 64.5%) or receiving operation (109/147, 74.1%) were prone to develop candidiasis, while aspergillosis was usually complicated in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) (25/51, 49.0%). The all-cause mortality rate was 25.9% (135/521), and patients aged ≥ 80 years were the riskiest (20/51, 39.2%). Lymphopenia (59.5% vs 17.3%, P < 0.001) was significant in deceased patients with mold infection. Higher proportion of non-survivors with invasive candidiasis received central venous catheterization (CVC) (68.4% vs 40.6%, P < 0.001) or indwelling urinary catheter (68.4% vs 46.3%, P =0.001).
Conclusion: IFD is a life-threatening complication especially in the oldest-old. Surveillance on lymphopenia, prompt treatment and reduce invasive procedures could benefit the prognosis.
Keywords: invasive fungal disease, elderly, mortality, hypoalbuminemia