111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

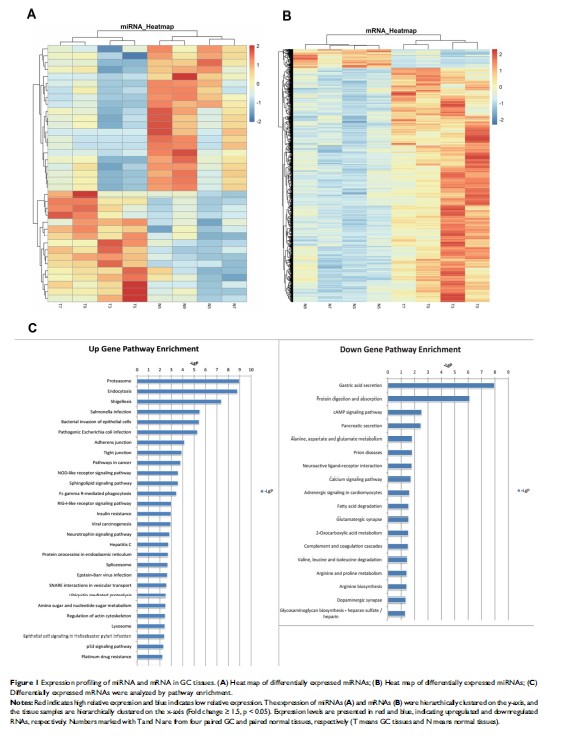
MicroRNA 图谱表明,miR-6165 可通过靶向 STRN4 抑制胃癌的迁移和侵袭
Authors Wang Z, Li Y, Cao J, Zhang W, Wang Q, Zhang Z, Gao Z, Ye Y, Jiang K, Wang S
Received 8 March 2019
Accepted for publication 11 February 2020
Published 3 March 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 1859—1869
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S208024
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr William Cho
Background: Recent studies showed that aberrant expression of miRNAs causes tumor-suppressing or promoting effects in various cancers including gastric cancer (GC). Our previous studies showed that lots of miRNAs and mRNA expressed differentially in GC and normal tissues. However, the critical miRNAs and mRNA need to be clarified.
Materials and Methods: Microarray sequencing was used to profile the differential expression of miRNAs and mRNA in GC and normal tissues. Bioinformatics analysis and database prediction were used to search the critical miRNAs and mRNA. Real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR), luciferase reporter assay, immunohistochemistry (IHC), wound healing assay and transwell assay were used to clarify the relationship between the target miRNAs and mRNA. Statistical analysis was used to seek their value of diagnosis and prognosis.
Results: We identified microRNA-6165 (miR-6165) as a novel cancer-related miRNA in GC through high-throughput microarray sequencing. By bioinformatics analysis and luciferase reporter assay, we found STRN4 was the target of miR-6165. Via a series of cell experiments, we determined that miR-6165 suppressed GC cells migration and invasion by targeting STRN4. Also, we discovered the potential diagnosis and prognosis value of miR-6165 and STRN4.
Conclusion: It was found that miR-6165 might suppress GC migration and invasion by targeting STRN4 in vitro, and the further research should focus more on the potential diagnosis and prognosis value of miR-6165 and STRN4 in gastric cancer patients.
Keywords: gastric cancer, miR-6165, STRN4, migration and invasion