111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

吸入麻醉药在肿瘤发生和肿瘤免疫中的作用
Authors Xu Y, Jiang W, Xie S, Xue F, Zhu X
Received 31 December 2019
Accepted for publication 12 February 2020
Published 4 March 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 1601—1609
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S244280
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sanjeev Srivastava
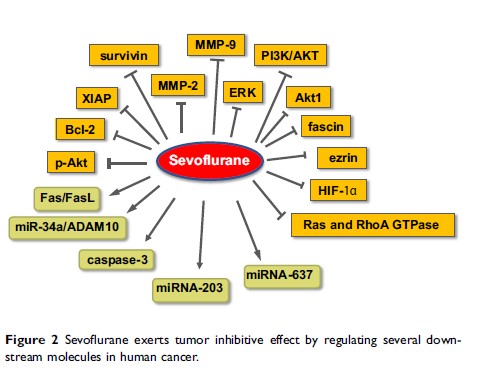
Abstract: Inhaled anesthetics are widely used for induction and maintenance of anesthesia during surgery, including isoflurane, sevoflurane, desflurane, haloflurane, nitrous oxide (N2O), enflurane and xenon. Nowadays, it is controversial whether inhaled anesthetics may influence the tumor progression, which urges us to describe the roles of different inhaled anesthetics in human cancers. In the review, the relationships among the diverse inhaled anesthetics and patient outcomes, immune response and cancer cell biology were discussed. Moreover, the mechanisms of various inhaled anesthetics in the promotion or inhibition of carcinogenesis were also reviewed. In summary, we concluded that several inhaled anesthetics have different immune functions, clinical outcomes and cancer cell biology, which could contribute to opening new avenues for selecting suitable inhaled anesthetics in cancer surgery.
Keywords: inhaled anesthetics, cancer, tumorigenesis, surgery, immune