111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

脂质参数与慢性肾脏疾病风险的关联:基于华南地区人口的纵向研究
Authors Wang X, Chen H, Shao X, Xiong C, Hong G, Chen J, Li X, You X, Gao P, Chen Y, Zou Z, Ning J, Xiao H, Zou H, Wei L
Received 31 August 2019
Accepted for publication 16 January 2020
Published 4 March 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 663—670
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DMSO.S229362
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Antonio Brunetti
Objective: To investigate which plasma lipid parameters are useful for detecting chronic kidney disease (CKD) in a Chinese population without known CKD or renal impairment.
Methods: This was a prospective study. In southern Chinese cities from 2012 to 2013, a total of 1037 subjects aged ≥ 18 years old received a survey. Logistic regression and multiple linear regression analyses were performed. The lipid parameters studied included total cholesterol (TC), triglycerides (TG), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (nHDL-C), TG/HDL-C ratio, TC/HDL-C ratio and nHDL-C/HDL-C ratio.
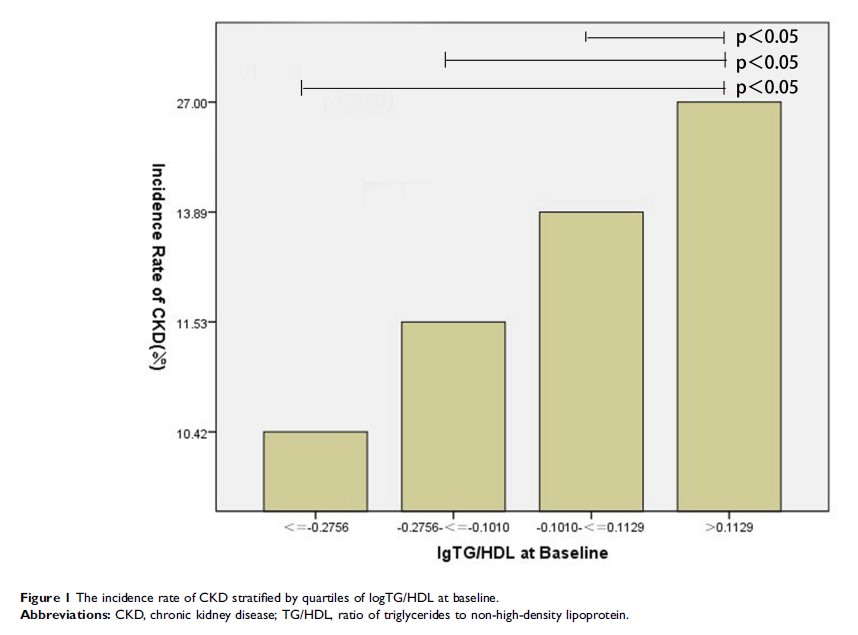
Results: After adjusting for confounding factors, the fourth percentile of logTG/HDL-C was observed to be an independent risk factor for CKD (OR = 2.453, P < 0.001), and the highest quantile of the logTG/HDL-C ratio was associated with a higher prevalence of CKD (P < 0.05). This risk was reduced when the model was adjusted with Insulin resistance (IR) (OR = 2.034, P < 0.05). In the group of women, glucose metabolism disorders, high uric acid, and obesity, this risk was increased. Multiple regression models showed that log TG and nonHDL-C/HDL-C were negatively correlated with eGFR (P < 0.05), while log TG and TC were positively correlated with logACR (P < 0.05). The area under the curve (ROC) of lgTG/HDL was 0.623 (p < 0.001).
Conclusion: The serum logTG/HDL-C ratio is the only suitable predictor of CKD, and IR may be the mechanism. This risk needs to be controlled in a specific population. Log TG and nonHDL-C/HDL-C were negatively correlated with eGFR, while log TG and TC were positively correlated with logACR.
Keywords: lipid, chronic kidney disease, CKD, urinary albumin to creatinine ratio, ACR, estimated glomerular filtration rate, eGFR