111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

确定中国重度抑郁症患者中的自杀意念:对中国医院实际病例进行研究得出的证据
Authors Ge F, Jiang J, Wang Y, Yuan C, Zhang W
Received 12 November 2019
Accepted for publication 21 January 2020
Published 4 March 2020 Volume 2020:16 Pages 665—672
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S238286
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yu-Ping Ning
Background: A growing body of research suggests that major depressive disorder (MDD) is one of the most common psychiatric conditions associated with suicide ideation (SI). However, how a combination of easily accessible variables built a utility clinically model to estimate the probability of an individual patient with SI via machine learning is limited.
Methods: We used the electronic medical record database from a hospital located in western China. A total of 1916 Chinese patients with MDD were included. Easily accessible data (demographic, clinical, and biological variables) were collected at admission (on the first day of admission) and were used to distinguish SI with MDD from non-SI using a machine learning algorithm (neural network).
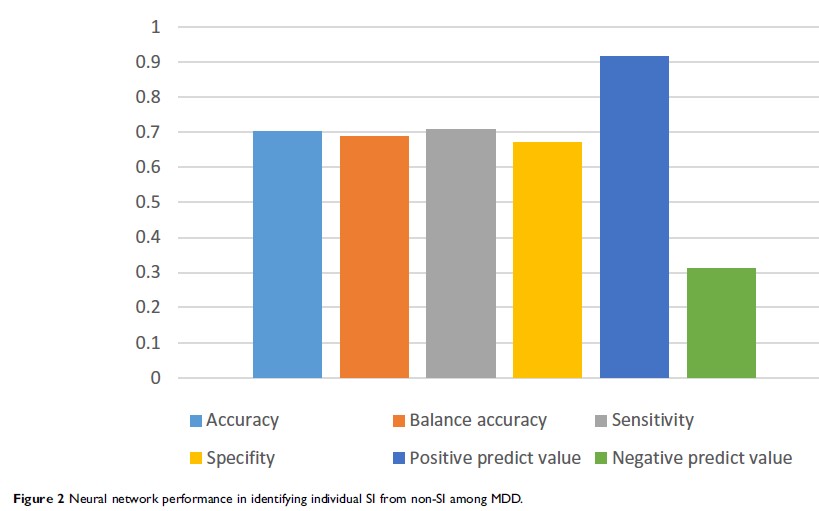
Results: The neural network algorithm distinguished 1356 out of 1916 patients translating into 70.08% accuracy (70.68% sensitivity and 67.09% specificity) and an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.76. The most relevant predictor variables in identifying SI from non-SI included free thyroxine (FT4), the total scores of Hamilton Depression Scale (HAMD), vocational status, and free triiodothyronine (FT3).
Conclusion: Risk for SI among patients with MDD can be identified at an individual subject level by integrating demographic, clinical, and biological variables as possible as early during hospitalization (at admission).
Keywords: depression, suicide ideation, real-world, machine learning