111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

上海地区 HIV+ 患者 LifeWindows 信息-动机-行为技能抗逆转录病毒治疗依从性问卷的可靠性和有效性
Authors Peng Z, Yu Y, Wei W, Hou Y, Sun Z, Wang Y, Zhang L, Zhou Y, Wang Q, Cai Y
Received 9 October 2019
Accepted for publication 1 February 2020
Published 5 March 2020 Volume 2020:14 Pages 507—515
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/PPA.S234041
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Naifeng Liu
Objective: The purpose of this article was to examine the validity and reliability of the LifeWindows Information–Motivation–Behavioral Skills Antiretroviral Therapy (ART) Adherence Questionnaire (LW-IMB-AAQ) among HIV+ patients in Shanghai.
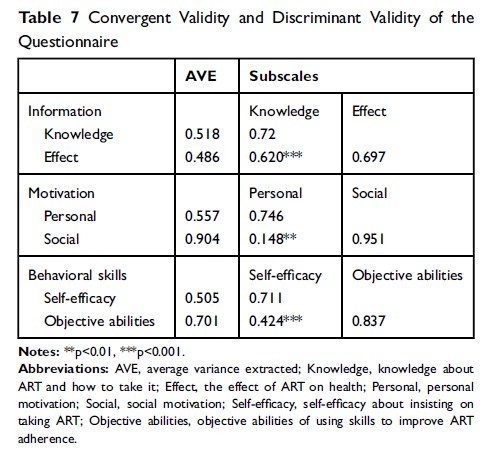
Methods: We surveyed 426 HIV+ patients in Shanghai’s Putuo District to examine the validity and reliability of the questionnaire. The questionnaire includes self-reported demographic characteristics, the modified version of the Community Programs for Clinical Research on AIDS Antiretroviral Medication Self-Report (CPCRA) and LW-IMB-AAQ. CPCRA was used to calculate ART adherence. LW-IMB-AAQ, including the information section, the motivation section and the behavioral skills section, was used to analyze patients’ ART adherence. We analyzed data by means, standard deviation, critical ratio, and item-total correlation. Reliability was assessed by internal consistency, split-half reliability, and test–retest reliability. Validity was assessed by exploratory factor analysis (EFA), confirmatory factor analysis (CFA), convergent validity and discriminant validity.
Results: Item analysis showed that except for motivation item 1, all items were acceptable. For reliability, Cronbach’s alpha coefficients for the three sections and the total scale were all higher than 0.7, with interclass correlation coefficients (ICC) all higher than 0.6 (p< 0.001). The Spearman–Brown coefficient for the total scale was 0.825. For validity, results showed that the information section could be divided into two subscales, motivation section and behavioral skills section could be divided into three and two subscales, respectively. The final model demonstrated good validity (p=0.471, χ 2/df=0.960, CFI=1.000, GFI=0.994 and RMSEA< 0.001) without motivation item 4.
Conclusion: Excluding motivation items 1 and 4, the LifeWindows Information–Motivation–Behavioral Skills ART Adherence Questionnaire (LW-IMB-AAQ) demonstrated good validity and reliability among HIV+ patients in Shanghai.
Keywords: HIV, validity, reliability, IMB model, China