111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

基于可生物降解的树突状聚合物、负载索拉非尼的纳米颗粒用于增强肝细胞癌的治疗效果
Authors Li Z, Ye L, Liu J, Lian D, Li X
Received 5 November 2019
Accepted for publication 21 February 2020
Published 5 March 2020 Volume 2020:15 Pages 1469—1480
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S237335
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Purpose: In spite of its enhanced efficacy and reduced side effects in clinical hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) therapy, the therapeutic efficacy of antitumor angiogenesis inhibitor sorafenib (SFB) is still restricted due to short in vivo half-life and drug resistance. Here, a novel SFB-loaded dendritic polymeric nanoparticle (NP-TPGS-SFB) was developed for enhanced therapy of HCC.
Methods: NP-TPGS-SFB was fabricated by encapsulating SFB with biodegradable dendritic polymers poly(amidoamine)-poly(γ-benzyl-L-Glutamate)-b-D-α-tocopheryl polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate (PAM-PBLG-b-TPGS).
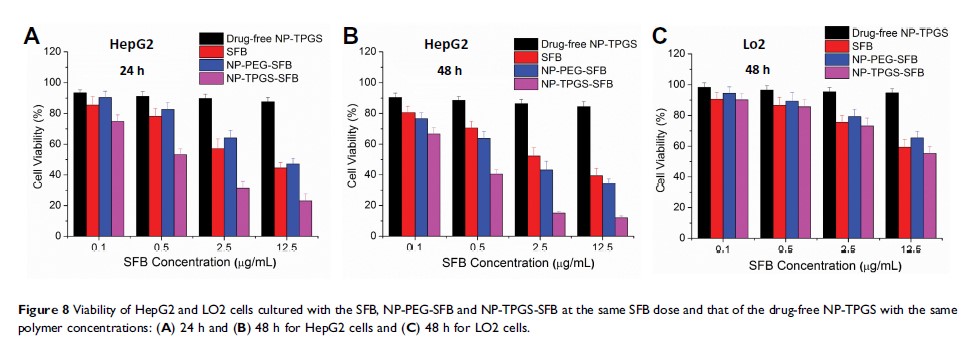
Results: NP-TPGS-SFB exhibited excellent stability and achieved acid-responsive release of SFB. It also exhibited much higher cellular uptake efficiency in HepG2 human liver cells than PEG-conjugated NP (NP-PEG-SFB). Furthermore, MTT assay confirmed that NP-TPGS-SFB induced higher cytotoxicity than NP-PEG-SFB and free SFB, respectively. Lastly, NP-TPGS-SFB significantly inhibited tumor growth in mice bearing HepG2 xenografts, with negligible side effects.
Conclusion: Our result suggests that NP-TPGS-SFB may be a novel approach for enhanced therapy of HCC with promising potential.
Keywords: dendritic block copolymer, sorafenib, enhanced therapy, TPGS, hepatocellular carcinoma