111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

LncRNA NCK1-AS1 通过下调 miR-143 促进膀胱癌患者的癌细胞增殖并增强细胞干性
Authors Qiao Z, Dai H, Zhang Y, Li Q, Zhao M, Yue T
Received 14 July 2019
Accepted for publication 22 January 2020
Published 6 March 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 1661—1668
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S223172
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Eileen O'Reilly
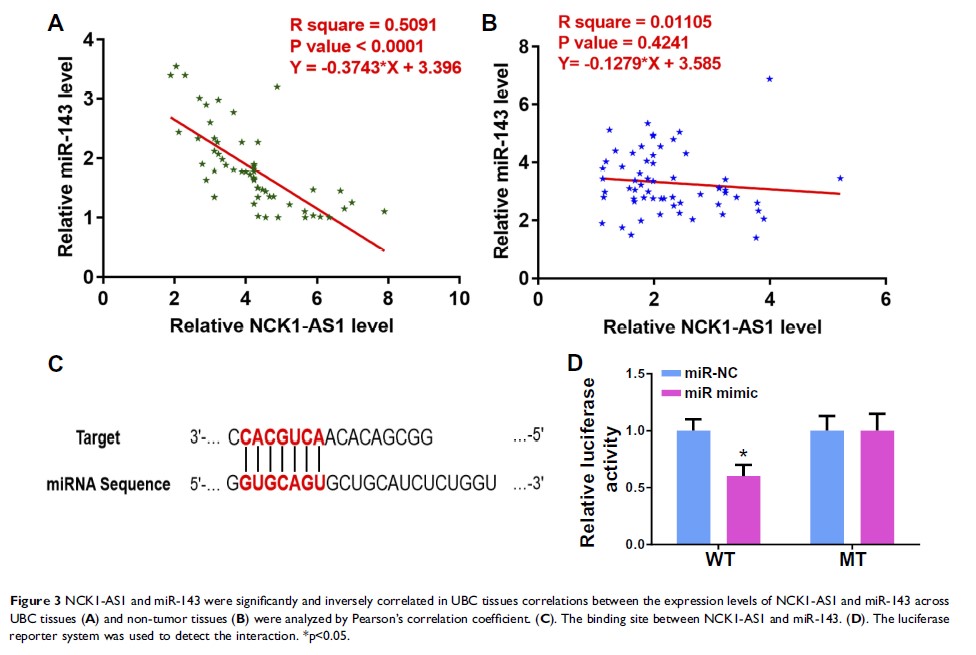
Background: Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) play critical and complex roles in regulating various biological processes of cancers. Our study aimed to investigate the involvement of lncRNA NCK1-AS1 in urinary bladder cancer (UBC).
Methods: qRT-PCR was used to detect the expression of lncRNA NCK1-AS1 and miR-143 in UBC tissues and cells. The dual-luciferase reporter system assays were used to confirm the interaction between NCK1-AS1 and miR-143, and flow cytometry assays were applied to examine the behavioral changes in HT-1376 and HT-1197 cell lines.
Results: It was observed that NCK1-AS1 was up-regulated, while miR-143 was down-regulated in tumor tissues than in adjacent healthy tissues of urinary bladder cancer (UBC) patients. A 5-year survival analysis showed that the survival rate of patients with high NCK1-AS1 level or low miR-143 level in tumor tissues appears relatively low. Correlation analysis revealed a significant inverse correlation between NCK1-AS1 and miR-143 in tumor tissues. Over-expression NCK1-AS1 reduced the expression level of miR-143, while elevating the level of miR-143 failed to affect NCK1-AS1 expression. NCK1-AS1 over-expression led to promoted proliferation and increased percentage of CD133+ (stemness) cells.
Conclusion: Therefore, NCK1-AS1 promotes cancer cell proliferation and increases cell stemness in UBC patients by down-regulating miR-143.
Keywords: NCK1-AS1, miR-143, urinary bladder cancer, survival, proliferation, stemness