111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

在分数比较任务中抑制整数偏差:一项事件相关电位的研究
Authors Fu X, Li X, Xu P, Zeng J
Received 27 November 2019
Accepted for publication 22 February 2020
Published 6 March 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 245—255
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/PRBM.S240263
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Professor Mei-chun Cheung
Introduction: People often use heuristics derived from natural number tasks to solve fraction comparison tasks. For instance, one may falsely consider a fraction with a larger natural number to be the larger in magnitude, as in the case of 1/5 vs 1/4. We hypothesized that inhibitory control was needed to overcome this type of bias.
Methods: To test the hypothesis, Event-related potentials (ERP) were collected when participants were conducting fraction comparison tasks that designed with the negative priming paradigm. Twenty-eight adult participants performed three types of fraction comparison tasks: congruent items, incongruent items and neutral items.
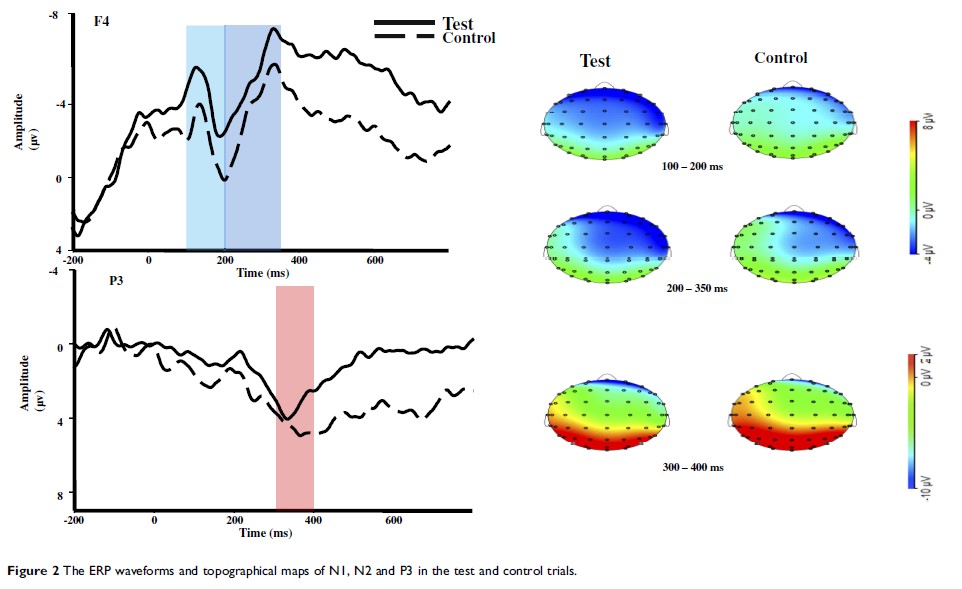
Results: We found a negative priming effect in terms of response time. Consistently, ERP results demonstrated larger N1 and N2 amplitudes and a smaller P3 amplitude in the test trial than in the control trial.
Conclusion: These findings indicated that adults still need to inhibit the “larger natural number-larger fraction” misleading strategy when solving fraction comparison tasks with common components.
Keywords: heuristics strategy, inhibitory control, fraction comparison, negative priming, event-related potential