111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

HIPK3 通过调节 miR-599/c-MYC 轴促进食管鳞状细胞癌的生长和转移
Authors Ba Y, Liu Y, Li C, Zhu Y, Xing W
Received 25 May 2019
Accepted for publication 10 January 2020
Published 6 March 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 1967—1978
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S217087
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Arseniy Yuzhalin
Background/Aims: this experimental design was based on HIPK3 to explore the pathogenesis of ESCC.
Methods: RT-qPCR was used to detect the expression of CircHIPK3 and miR-599 in ESCC tissues and cell lines.CCK-8, colony formation, flow cytometry and transwell assay were used to detect the effects of CircHIPK3 and miR-599 on tumor cell proliferation, apoptosis and migration and invasion. Target gene prediction and screening, luciferase reporter assays were used to validate downstream target genes of CircHIPK3 and miR-599.mRNA and protein expression of c-MYC were detected by RT-qPCR and Western blotting. The tumor changes in mice were detected by in vivo experiments in nude mice.
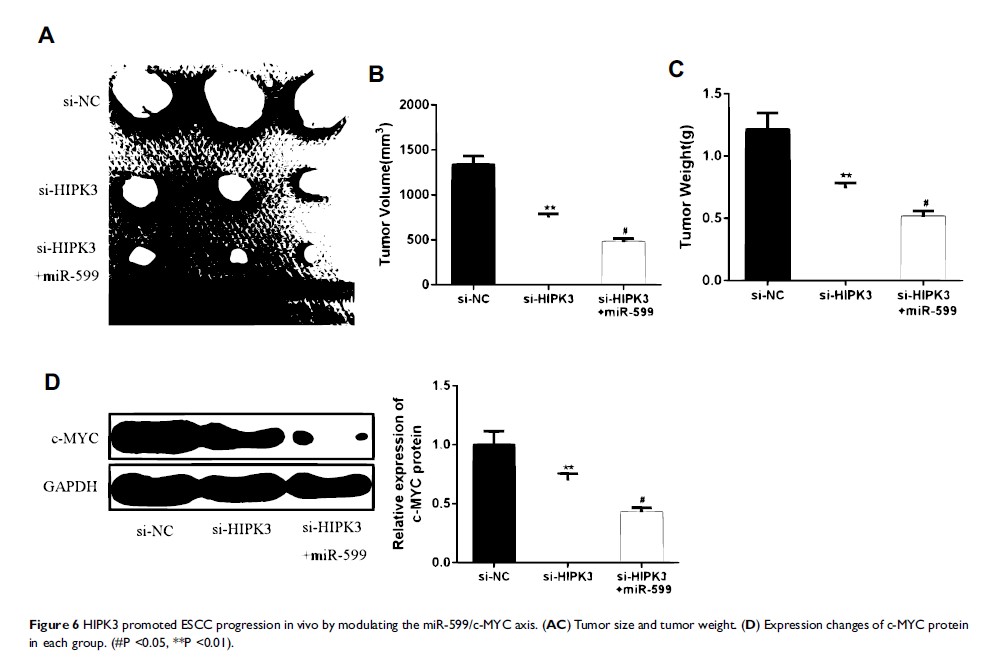
Results: HIPK3 was highly expressed in ESCC tissues and cell lines. In addition, HIPK3 expression levels were associated with advanced TNM stage, lymph node metastasis and tumor size. Moreover, HIPK3 was significantly promoted cell proliferation and migration of ESCC cells. In addition, HIPK3 was able to inhibit miRNA-599 expression and up-regulate the expression level of c-MYC. Finally, the results of in vivo animal models confirmed that HIPK3 promoted ESCC progression by modulating the miR-599/c-MYC axis.
Conclusion: HIPK3 can regulate the proliferation of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells by regulating miR-599/c-MYC axis, thereby inhibiting the occurrence and development of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Keywords: esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, HIPK3, miR-599, c-MYC, proliferation