111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

通过原位激活免疫应答,免疫治疗纳米制剂经鼻给药可用于神经胶质瘤治疗
Authors Yin P, Li H, Ke C, Cao G, Xin X, Hu J, Cai X, Li L, Liu X, Du B
Received 29 November 2019
Accepted for publication 25 February 2020
Published 6 March 2020 Volume 2020:15 Pages 1499—1515
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S240551
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
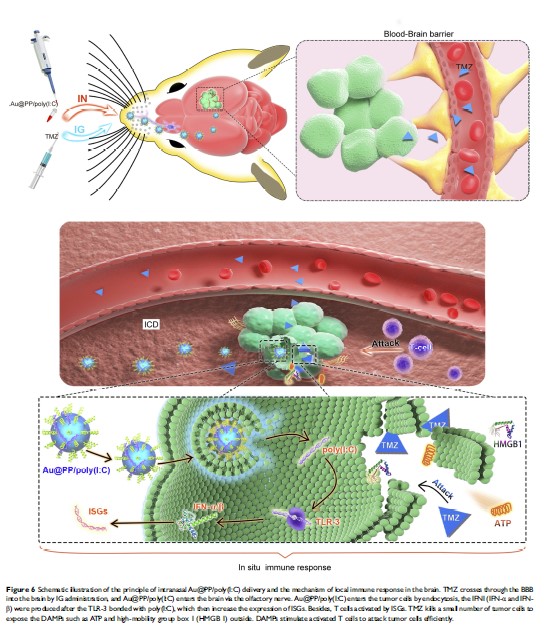
Purpose: Some chemotherapeutics have been shown to induce both the release of damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) and the production of type I interferon (IFN-I), leading to immunogenic cell death (ICD). However, the standard chemotherapy drug for glioma, temozolomide (TMZ), cannot induce ICD as it cannot activate IFN-I signaling. Moreover, inefficient delivery of immunostimulants across the blood–brain barrier (BBB) is the main obstacle to overcome in order to induce local immune responses in the brain.
Methods: A new oligonucleotide nanoformulation (Au@PP)/poly(I:C)) was constructed by coating gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) with methoxypolyethylene glycol (mPEG)-detachable (d)-polyethyleneimine (PEI) (Au@PP) followed by inducing the formation of electrostatic interactions with polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid (poly(I:C)). Intracranial GL261 tumor-bearing C57BL/6 mice were used to explore the therapeutic outcomes of Au@PP/poly(I:C) plus TMZ in vivo. The anti-tumor immune response in the brain induced by this treatment was analyzed by RNA sequencing and immunohistochemical analyses.
Results: Au@PP/poly(I:C) induced IFN-I production after endocytosis into glioma cells in vitro. Additionally, Au@PP/poly(I:C) was efficiently accumulated in the glioma tissue after intranasal administration, which allowed the nanoformulation to enter the brain while bypassing the BBB. Furthermore, Au@PP/poly(I:C) plus TMZ significantly improved the overall survival of the tumor-bearing mice compared with group TMZ only. RNA sequencing and immunohistochemical analyses revealed efficient immune response activation and T lymphocyte infiltration in the Au@PP/poly(I:C) plus TMZ group.
Conclusion: This study demonstrates that intranasal administration of Au@PP/poly(I:C) combined with TMZ induces ICD, thereby stimulating an in situ immune response to inhibit glioma growth.
Keywords: AuNPs, poly(I:C), intranasal administration, immunogenic cell death, in situ immune response activation