111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

LncRNA-SNHG16 沉默可抑制前列腺癌细胞的生长、下调 GLUT1 表达并减少葡萄糖摄取
Authors Shao M, Yu Z, Zou J
Received 17 September 2019
Accepted for publication 10 January 2020
Published 9 March 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 1751—1757
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S231370
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Eileen O'Reilly
Background: lncRNA-SNHG16 was identified as an oncogene in many cancers, but its involvement in prostate carcinoma is unknown.
Material and Method: Expression of lncRNA-SNHG16 and glucose transporter 1 (GLUT-1) in 52 prostate carcinoma tissues and 36 normal prostate tissues was analyzed by RT-qPCR. Transfections were performed to analyze gene interactions. Cell proliferation was analyzed by cell proliferation assay.
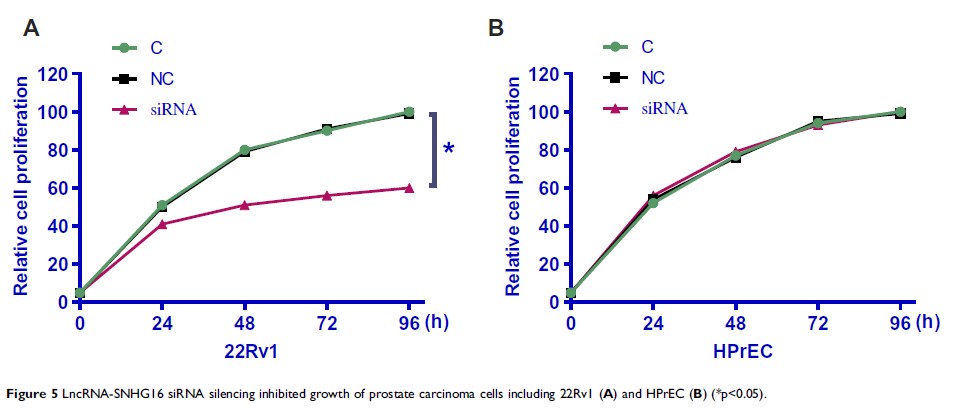
Results: Overexpression of lncRNA-SNHG16 effectively distinguished prostate carcinoma patients from normal ones. Expression levels of lncRNA-SNHG16 and GLUT-1 mRNA were significantly and positively correlated across prostate carcinoma tissues. In vitro cancer cell experiments revealed that lncRNA-SNHG16 siRNA silencing downregulated the expressions of GLUT-1 and reduced glucose uptake. lncRNA-SNHG16 siRNA silencing also significantly inhibited prostate carcinoma cell proliferation. However, lncRNA-SNHG16 siRNA silencing did not affect the normal prostate.
Conclusion: In conclusion, lncRNA-SNHG16 might be a possible treatment target for prostate cancer.
Keywords: prostate carcinoma, SNHG16, glucose transporter 1