111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

从中国血液感染新生儿体内收集的产生 IMP-4 的肺炎克雷伯菌 ST1873 菌株的表征
Authors Xu J, Lin W, Chen Y, He F
Received 26 January 2020
Accepted for publication 23 February 2020
Published 9 March 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 773—779
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IDR.S247341
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sahil Khanna
Purpose: Imipenemase (IMP), an Ambler class B metallo-β-lactamase, is an important carbapenemase that confers resistance to almost all β-lactams. In this study, we characterized the genomic feature of an IMP-4-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae ST1873 strain, a rare sequence type (ST) isolated from an infant with a bloodstream infection in China.
Patients and Methods: K. pneumoniae strain, BKP19, was collected from a bloodstream infection in an infant who was hospitalized at the department of paediatrics. The whole genome sequence of the strain was sequenced using the Illumina NovaSeq 6000 platform and long-read MinION sequencer. Multilocus sequence typing, antimicrobial resistance gene identification, plasmid and phylogenetic relationship analysis of the strain were analysed by various bioinformatics approaches.
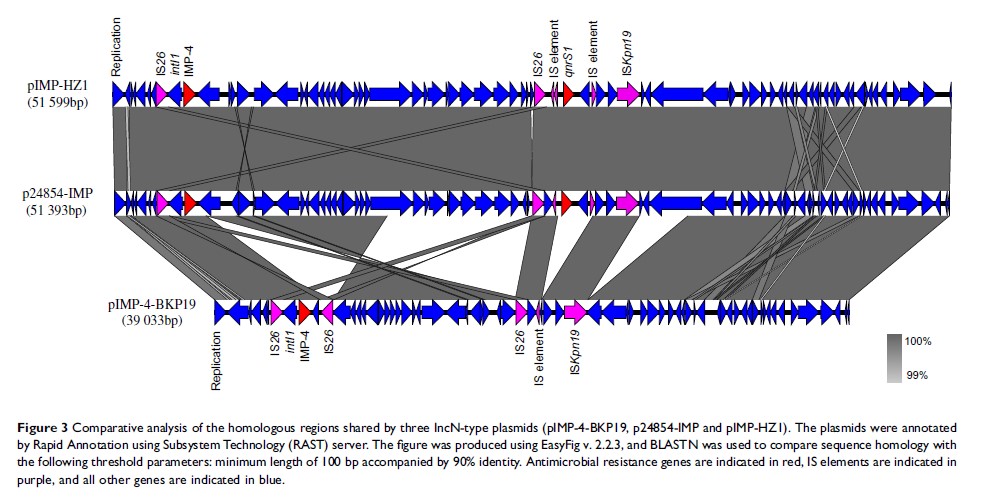
Results: K. pneumoniae BKP19 was resistant to multiple antimicrobials, including carbapenems. Eleven antimicrobial resistance genes corresponding to beta-lactam resistance, quinolone resistance, phenicol resistance and fosfomycin resistance could be identified in the genome. The carbapenem resistance gene bla IMP-4 was located in an IS26-associated class 1 integron of an IncN-type plasmid with 39,033 bp (pIMP-4-BKP19). Sequence alignment revealed that pIMP-4-BKP19 is closely related to the common plasmid carrying IMP-4 in K. pneumoniae (pIMP-HZ1-like plasmid) but is smaller, lacking the quinolone resistance gene qnrS1 and multiple tra gene orthologs. Conjugation experiment revealed that pIMP-4-BKP19 is a non-conjugative plasmid. According to in silico MLST analysis, K. pneumoniae strain BKP19 belongs to a sporadic clone ST1873.
Conclusion: In summary, our study reports the first genome sequence of a K. pneumoniae ST1873 strain harbouring the class B β-lactamase bla IMP-4 in an IncN-type plasmid recovered from an infant with a bloodstream infection in China. Considering the global emergence of IMP-4 carbapenemase, more attention must be paid to prevent its future prevalence.
Keywords: Klebsiella pneumoniae , bla IMP-4, IncN plasmid, ST1873, bloodstream infection