111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

HANR 通过 miR-29b/ATG9A 轴增强肝细胞癌中与自噬相关的索拉非尼耐药性
Authors Shi Y, Yang X, Xue X, Sun D, Cai P, Song Q, Zhang B, Qin L
Received 5 September 2019
Accepted for publication 12 December 2019
Published 9 March 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 2127—2137
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S229913
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Nicola Silvestris
Background: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most common malignancies worldwide and chemoresistance is the main obstacle for effective treatments of HCC. Accumulating studies indicated that long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) contribute to the chemoresistance of human carcinoma. However, the functional role of HANR in autophagy-mediated chemoresistance of HCC is unknown.
Methods: The expressions of HANR, miR-29b and ATG9A in tissues and cell lines were detected by real-time quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR). The expression of autophagy-related protein LC3-I and LC3-II was evaluated by Western blotting. The cell viability and apoptosis were examined by CCK-8 and flow cytometry, respectively. Bioinformatics analysis and luciferase activity assay were applied to determine the downstream target gene of HANR or miR-29b. Xenograft experiment was used to detect the effect of HANR on tumor growth.
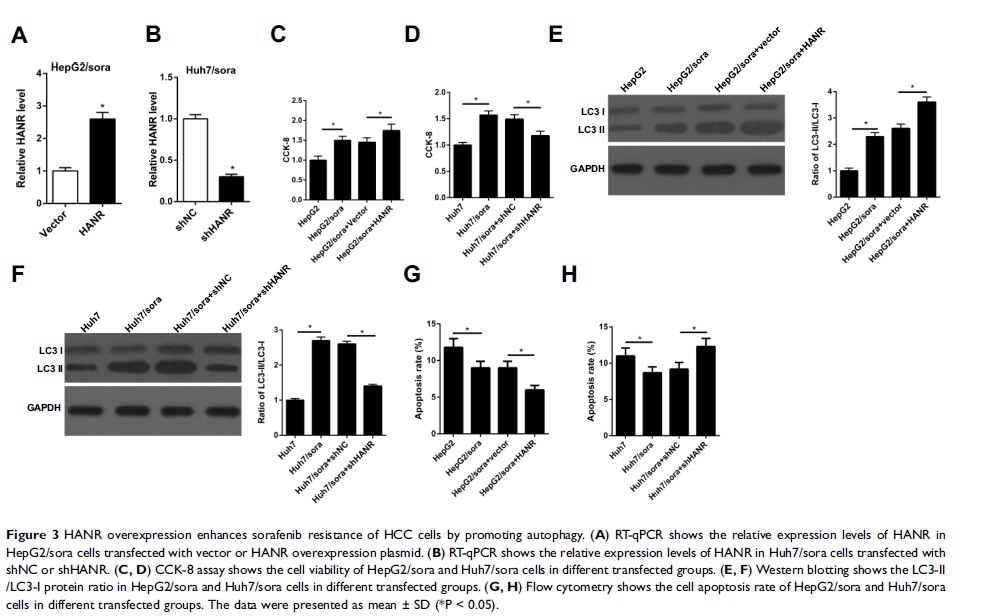
Results: In the present study, we demonstrated that HANR was notably overexpressed in sorafenib-resistant HepG2 (HepG2/sora) and sorafenib-resistant Huh7 (Huh7/sora) cells, and HANR enhanced sorafenib resistance by facilitating autophagy in HepG2/sora and Huh7/sora cells. Furthermore, we demonstrated that miR-29b could directly interact with HANR and abolished HANR-induced sorafenib resistance by suppressing autophagy in HepG2/sora and Huh7/sora cells. Moreover, ATG9A was validated as a target of miR-29b and its overexpression obviously reversed the inhibitory effect of miR-29b on sorafenib resistance and autophagy. In addition, HANR could act as a competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) to upregulate ATG9A expression by sponging miR-29b. Hence, HANR increased autophagy-related sorafenib resistance via inhibiting the miR-29b/ATG9A axis in HepG2/sora and Huh7/sora cells, indicating that it may be a potential target to prevent chemoresistance of HCC.
Conclusion: Our study revealed HANR enhanced sorafenib resistance by acting as an autophagy promoter by regulating miR-29b/ATG9A axis in sorafenib-resistant HCC cells and might provide potential therapeutic strategies for HCC treatment.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma, HCC, autophagy, HANR, miR-29b, ATG9A