111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

长非编码 RNA DLEU1 上调 BIRC6 表达,通过 miR-381-3p 竞争性海绵化促进鼻咽癌的顺铂耐药性
Authors Li H, Huang J, Yu S, Lou Z
Received 6 November 2019
Accepted for publication 15 February 2020
Published 9 March 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 2037—2045
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S237456
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Leo Jen-Liang Su
Background: Cisplatin (DDP) resistance has become an obstacle to chemotherapy for nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) patients. Recent evidences indicate that long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) are involved in tumorigenesis and chemoresistance. However, the potential role of lncRNAs in NPC progression remains largely unknown.
Methods: First, lncRNA expression profiling in NPC was performed via microarray analysis. To explore the involvement of DLEU1 in DDP resistance, loss-of-function experiments were employed in vitro and in vivo. Bioinformatics analysis, luciferase reporter assay, qRT-PCR, and Western blot assays were used to investigate the underlying mechanisms.
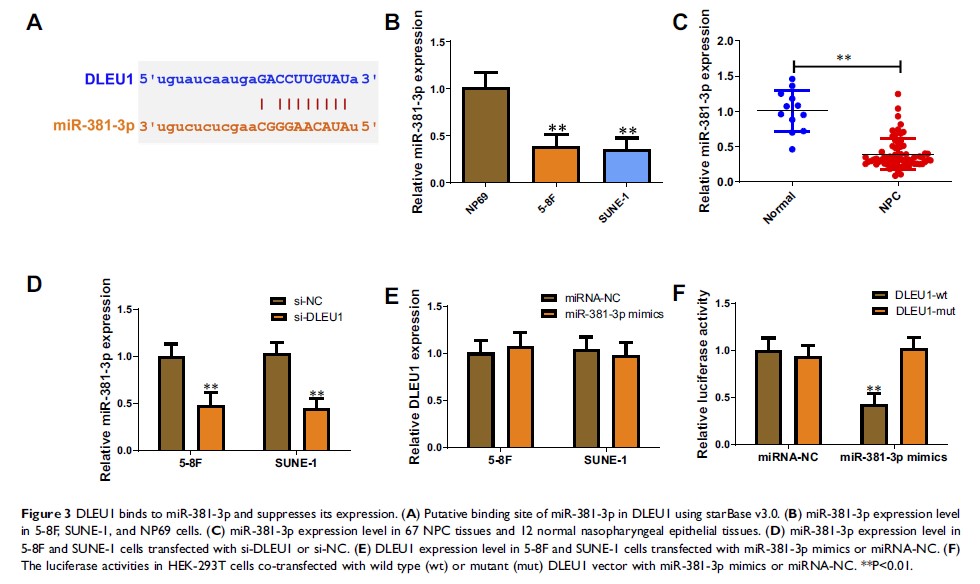
Results: Here, we identified 153 differentially expressed lncRNAs. Among them, DLEU1 was remarkably up-regulated in NPC tissues and associated with worse outcome. Knock-down of DLEU1 could sensitize NPC cells to DDP in vitro and in vivo. Further investigations revealed that DLEU1 positively regulated BIRC6 expression via its competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) activity on miR-381-3p. We also observed that BIRC6 overexpression or miR-381-3p silence could significantly reverse DLEU1-dependent DDP resistance.
Conclusion: Our data suggest that DLEU1 acts as an oncogene to promote DDP resistance and BIRC6 expression in NPC through interacting with miR-381-3p, which may help to develop new strategy against NPC chemoresistance.
Keywords: DLEU1, cisplatin resistance, nasopharyngeal carcinoma, BIRC6