111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

术前炎症评分及 TNM 分期与乳头状甲状腺癌患者复发的相关性:一项回顾性、多中心分析
Authors Chen W, Wei T, Li Z, Gong R, Lei J, Zhu J, Huang T
Received 19 November 2019
Accepted for publication 25 January 2020
Published 11 March 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 1809—1818
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S239296
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Seema Singh
Background: The neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR), and prognostic nutritional index (PNI) have been reported to be prognostic biomarkers in various cancers. Our study evaluated whether the preoperative NLR, PLR and PNI predicted tumor-node-metastasis (TNM) stage and recurrence in papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) patients.
Methods: A total of 1873 patients with PTC from 9 centers in mainland China were retrospectively assessed. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were generated, and Kaplan-Meier analyses were performed to evaluate the prognostic value of inflammation-based scores. Univariate and multivariate analyses were conducted to identify risk factors for recurrence.
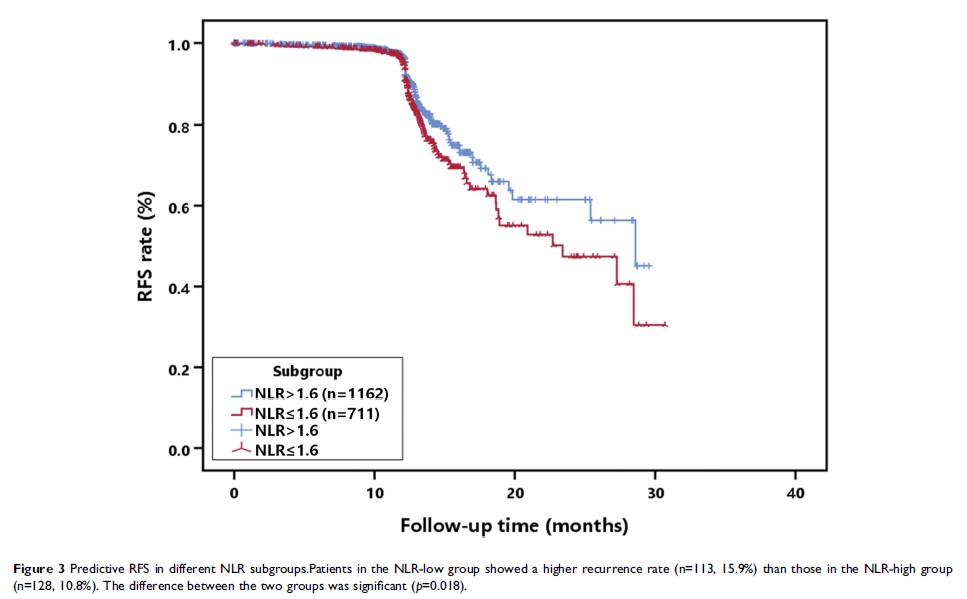
Results: A decreased PNI and an increased PLR were predictive of TNM stage (p =0.005 and p =0.030, respectively), while a decreased NLR was predictive of recurrence (p =0.040). Univariate and multivariate analyses indicated that N1 status (odds ratio (OR), 1.898; 95% confidence interval (CI), 1.253– 2.874; p =0.002), NLR≤ 1.6 (OR, 1.596; 95% CI, 1.207– 2.111; p =0.001) and PNI≤ 53.1 (OR, 1.511; 95% CI, 1.136– 2.009; p =0.005) were independent factors that predicted recurrence.
Conclusion: The NLR, PLR and PNI have predictive value for TNM stage and recurrence in patients with PTC, but their predictive efficiency is limited. Caution should be used when considering clinical applications of inflammation-based scores.
Keywords: inflammation-based scores, papillary thyroid carcinoma, lymph node metastasis, prognosis