111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

关于高脂血症诊断及自动提供诊断标志物的深度学习方法
Authors Liu Y, Zhang Q, Zhao G, Liu G, Liu Z
Received 16 December 2019
Accepted for publication 26 February 2020
Published 11 March 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 679—691
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DMSO.S242585
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Antonio Brunetti
Introduction: The research of auxiliary diagnosis has always been one of the hotspots in the world. The implementation of auxiliary diagnosis support algorithm for medical text data faces challenges with interpretability and creditability. The improvement of clinical diagnostic techniques means not only the improvement of diagnostic accuracy but also the further study of diagnostic basis. Traditional research methods for diagnostic markers often require a large amount of time and economic costs. Research objects are often dozens of samples, and it is, therefore, difficult to synthesize large amounts of data. Therefore, the comprehensiveness and reliability of traditional methods have yet to be improved. Therefore, the establishment of a model that can automatically diagnose diseases and automatically provide a diagnostic basis at the same time has a positive effect on the improvement of medical diagnostic techniques.
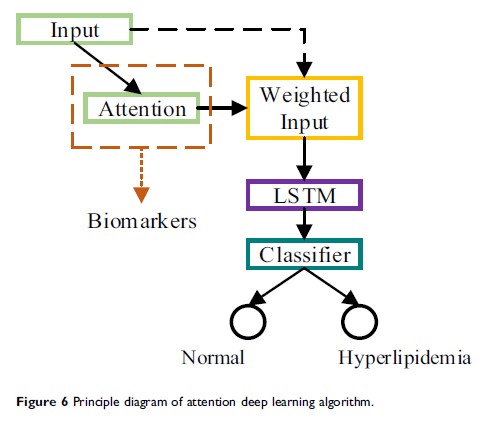
Methods: Here, we established an auxiliary diagnostic tool based on attention deep learning algorithm to diagnostic hyperlipemia and automatically predict the corresponding diagnostic markers using hematological parameters. In this paper, we not only demonstrated the ability of the proposed model to automatically diagnose diseases using text-based medical data, such as physiological parameters, but also demonstrated its ability to forecast disease diagnostic markers. Human physiological parameters are used as input to the model, and the doctor’s diagnosis results as an output. Through the attention layer, the degree of attention of the model to different physiological parameters can be obtained, that is, the model provides a diagnostic basis.
Results: It achieved 94% ACC, 97.48% AUC, 96% sensitivity and 92% specificity with the test dataset. All the above samples are drawn from clinical practice. Moreover, the model predicted the diagnostic markers of hyperlipidemia by the attention mechanism, and the results were fully agreeable to the golden criteria.
Discussion: The auxiliary diagnosis system proposed in this paper not only achieves the accurate and robust performance, and can be used for the preliminary diagnosis of patients, but also showing its great potential to discover new diagnostic markers. Therefore, it not only can improve the efficiency of clinical diagnosis but also shorten the research period of researching a diagnosis basis to an extent. It has a positive significance to the development of the medical diagnosis level.
Keywords: automatic predictive diagnostic markers, automatic diagnosis, attention mechanism, hyperlipemia, artificial intelligence