111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

B7-H3 通过 JAK2/STAT3/Slug 依赖性信号传导通路调节神经胶质瘤的生长和细胞侵袭
Authors Zhong C, Tao B, Chen Y, Guo Z, Yang X, Peng L, Xia X, Chen L
Received 9 November 2019
Accepted for publication 24 February 2020
Published 12 March 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 2215—2224
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S237841
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr William Cho
Purpose: The aim of this study was to explore the potential role of B7-H3 in malignant glioma progression and identify an innovative approach in clinical glioma therapy.
Methods: The protein expression of B7-H3 in high- and low-grade tumor tissues from glioma patients was assessed by immunohistochemistry. The proliferative and invasive ability of B7-H3-overexpressing or knockout glioma cells was analyzed in vitro and in vivo by CCK-8 assay and an orthotopic mouse glioma model, respectively. Activation of the JAK2/STAT3/Slug signaling pathway and epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) was examined by Western blotting and immunofluorescence. The anticancer effects of napabucasin (NAP) and temozolomide (TMZ) were analyzed in an orthotopic mouse glioma model.
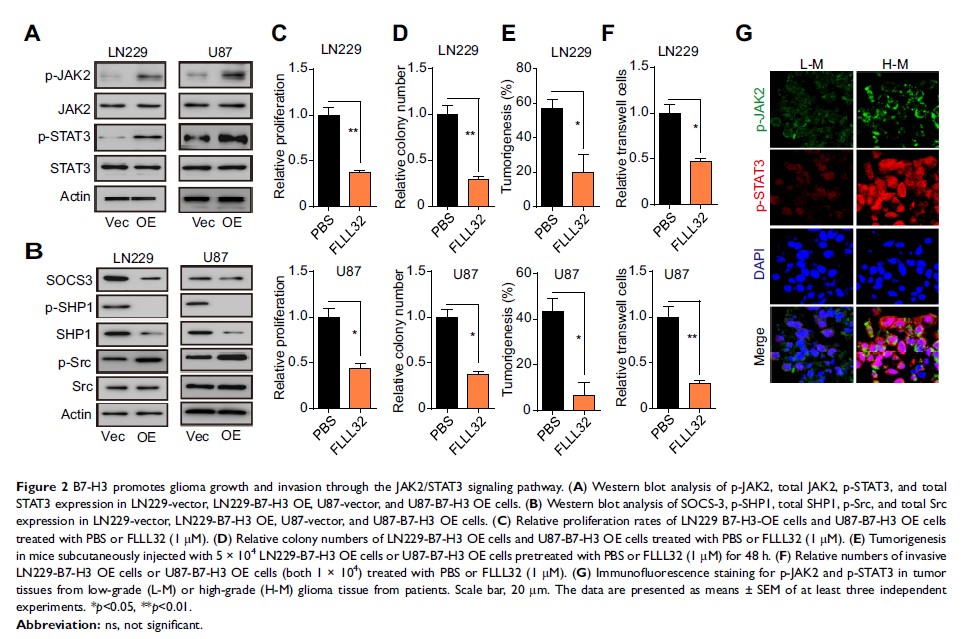
Results: The expression of B7-H3 was higher in high-grade than in low-grade tumor tissues from glioma patients. In line with this, overexpression of B7-H3 enhanced glioma cell proliferation, induced sustained glioma growth, and promoted glioma cell invasion in vitro and in vivo. Moreover, these effects were mediated through the activation of the JAK2/STAT3/Slug signaling pathway in B7-H3 overexpression glioma cells. We also found that B7-H3 induced EMT processes through downregulation of E-cadherin and upregulation of MMP-2/-9 expression, resulting in enhanced invasion of glioma cells. Finally, we show that the combination of NAP and TMZ significantly suppressed glioma growth and glioma cell invasion, both in vitro and in vivo.
Conclusion: B7-H3 overexpression facilitated sustained glioma growth and promoted glioma cell invasion through a JAK2/STAT3/Slug-dependent signaling pathway. Application of the STAT3 inhibitor NAP significantly suppressed glioma growth and invasion, and has potential as a therapeutic strategy for the treatment of glioma.
Keywords: B7-H3, glioma, JAK2/STAT3/Slug, temozolomide