111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

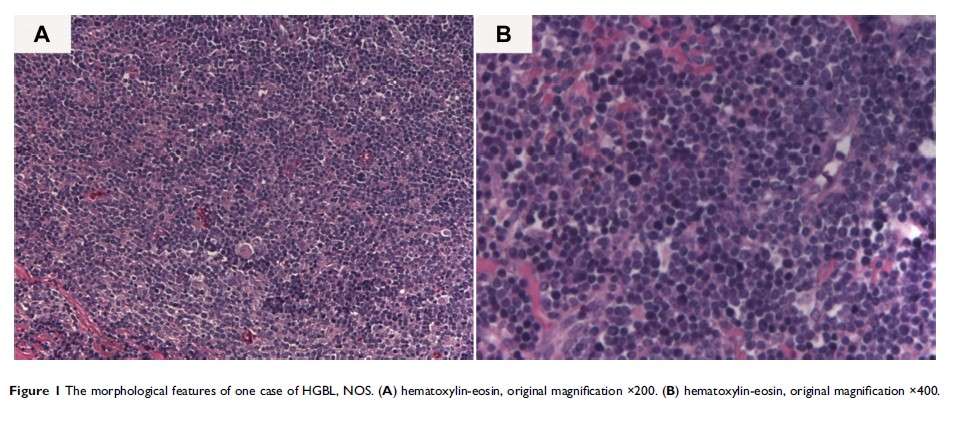
高级别 B 细胞淋巴瘤(非特指性):41 个病例的报告
Authors Li J, Liu X, Yao Z, Zhang M
Received 26 December 2019
Accepted for publication 3 March 2020
Published 13 March 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 1903—1912
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S243753
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yong Teng
Purpose: To analyze the clinical and pathological characteristics, treatment, and prognosis of high-grade B-cell lymphomas, not otherwise specified (HGBL, NOS), and to increase awareness of this type of lymphoma.
Patients and Methods: We collected clinical and pathological data of 41 cases of newly diagnosed HGBL, NOS, and analyzed diagnosis, prognosis and treatment to examine progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS).
Results: Among the 41 cases studied, the median PFS was 6.0 months and the median OS was 18.0 months. Compared with patients treated with the R-CHOP regimen, patients treated with a high-intensity chemotherapy (DA-EPOCH-R, R-CODOX-M/IVAC, or R-Hyper-CVAD) had superior PFS and OS (PFS: χ 2=4.173, P =0.041; OS: χ 2=5.200, P =0.023). A subgroup analysis showed that the OS for the double-expressor lymphoma (DEL) was inferior to that for the non-DEL (χ 2=4.563, P =0.033), and this trend was also seen for the single-hit lymphoma with MYC rearrangement (SHL) and the non-SHL (χ 2=4.955, P =0.026). Patients with low International Prognostic Index (IPI) scores (≤ 2) had better survival rates than those with high scores (> 2) (PFS: χ 2=6.482, P =0.011; OS: χ 2=10.156, P =0.001).
Conclusion: HGBL, NOS is associated with a high degree of malignancy, short survival period, and substantial extranodal involvement. High-intensity chemotherapy may improve patient prognosis. While IPI scores statistically correlated with the prognosis, SHL and DEL correlated with an inferior survival rate. New and improved treatments will be needed for HGBL, NOS.
Keywords: HGBL, NOS, clinical and pathological, treatment, prognosis