111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

重楼皂苷 VI 通过活性氧簇介导下的 JNK 和 P38 活化,诱导胶质瘤中的细胞凋亡和自噬
Authors Liu W, Chai Y, Hu L, Wang J, Pan X, Yuan H, Zhao Z, Song Y, Zhang Y
Received 1 January 2020
Accepted for publication 2 March 2020
Published 13 March 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 2275—2288
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S243953
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Leo Jen-Liang Su
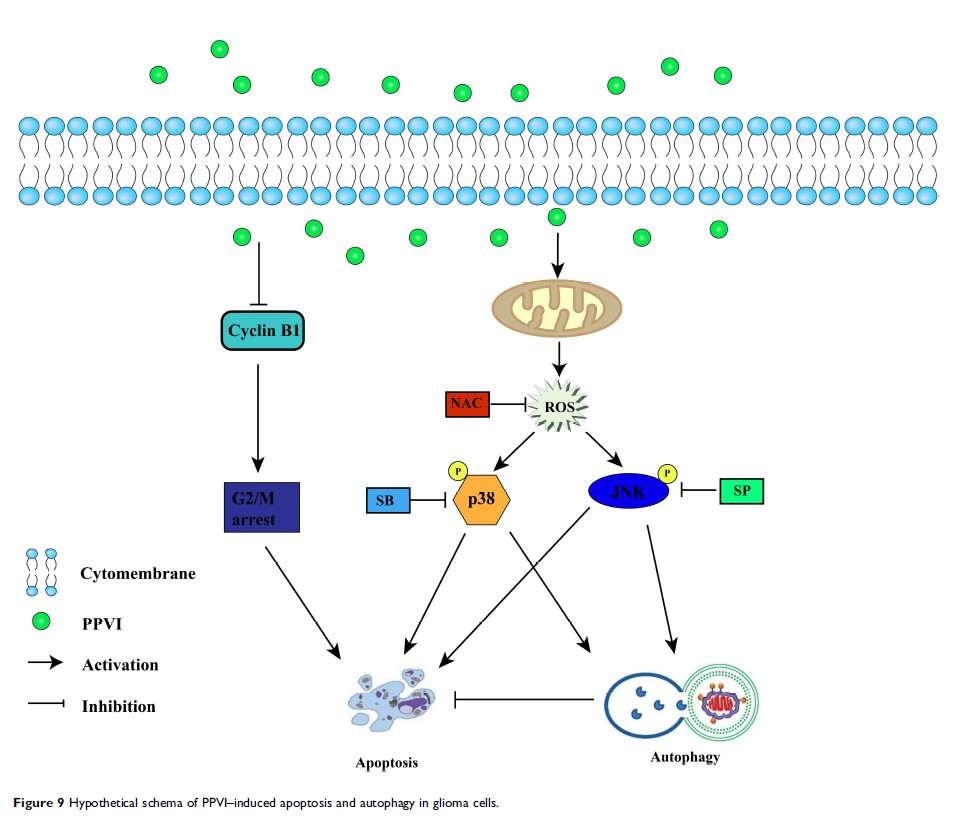
Background: Polyphyllin VI (PPVI), a bioactive component derived from a traditional Chinese herb Paris polyphylla, exhibits potential antitumor activity against hepatocellular carcinoma, as well as breast and lung cancers. However, its effect on glioma remains unknown.
Methods: Five glioma cell lines (U251, U343, LN229, U87 and HEB) and an animal model were employed in the study. Anti-proliferation effects of PPVI were first determined using CCK-8 cell proliferation and clone formation assays, then reactive oxygen species (ROS), cell cycle progression and apoptosis effects measured by flow cytometry. The effect of PPVI on protein expression was quantified by Western blot analysis.
Results: Data showed that PPVI inhibited the proliferation of glioma cell lines by modulating the G2/M phase. Additionally, incubation of cells with PPVI promoted apoptosis, autophagy, increased accumulation of ROS and activated ROS-modulated JNK and p38 pathways. On the other hand, N-acetyl cysteine, a ROS inhibitor, attenuated PPVI-triggered effects. Furthermore, JNK and p38 inhibitors ameliorated PPVI-triggered autophagy and apoptosis in glioma cells. In vivo assays showed that PPVI inhibited tumor growth of U87 cell line in nude mice.
Conclusion: Overall, these data suggested that PPVI might be an effective therapeutic agent for glioma.
Keywords: polyphyllin VI, glioma, autophagy, apoptosis, reactive oxygen species