111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

功能化的金、银双金属纳米颗粒,使用耐辐射异常球菌蛋白提取物来介导有毒染料孔雀石绿的降解
Authors Weng Y, Li J, Ding X, Wang B, Dai S, Zhou Y, Pang R, Zhao Y, Xu H, Tian B, Hua Y
Received 1 November 2019
Accepted for publication 22 February 2020
Published 16 March 2020 Volume 2020:15 Pages 1823—1835
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S236683
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Thomas J Webster
Background: Biodegradation of toxic organic dye using nanomaterial-based microbial biocatalyst is an ecofriendly and promising technique.
Materials and Methods: Here, we have investigated the novel properties of functionalized Au-Ag bimetallic nanoparticles using extremophilic Deinococcus radiodurans proteins (Drp-Au-AgNPs) and their degradation efficiency on the toxic triphenylmethane dye malachite green (MG).
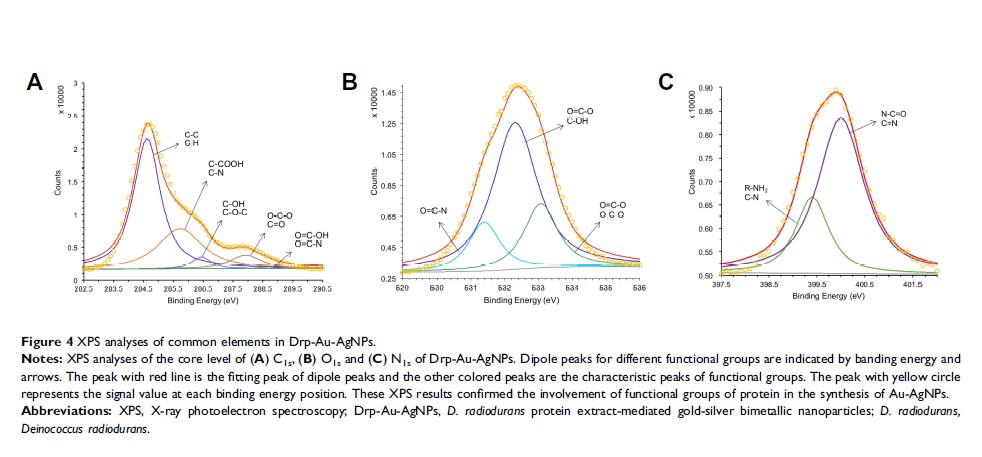
Results and Discussion: The prepared Drp-Au-AgNPs with an average particle size of 149.8 nm were capped by proteins through groups including hydroxyl and amide. Drp-Au-AgNPs demonstrated greater degradation ability (83.68%) of MG than D. radiodurans cells and monometallic AuNPs. The major degradation product was identified as 4-(dimethylamino) benzophenone, which is less toxic than MG. The degradation of MG was mainly attributed to the capping proteins on Drp-Au-AgNPs. The bimetallic NPs could be reused and maintained MG degradation ability (> 64%) after 2 cycles.
Conclusion: These results suggest that the easily prepared Drp-Au-AgNPs have potential applications as novel nanomedicine for MG detoxification, and nanomaterial for biotreatment of a toxic polyphenyl dye-containing wastewater.
Keywords: bimetallic nanoparticles, Deinococcus radiodurans , biodegradation, toxic triphenylmethane dye, malachite green, detoxification