111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

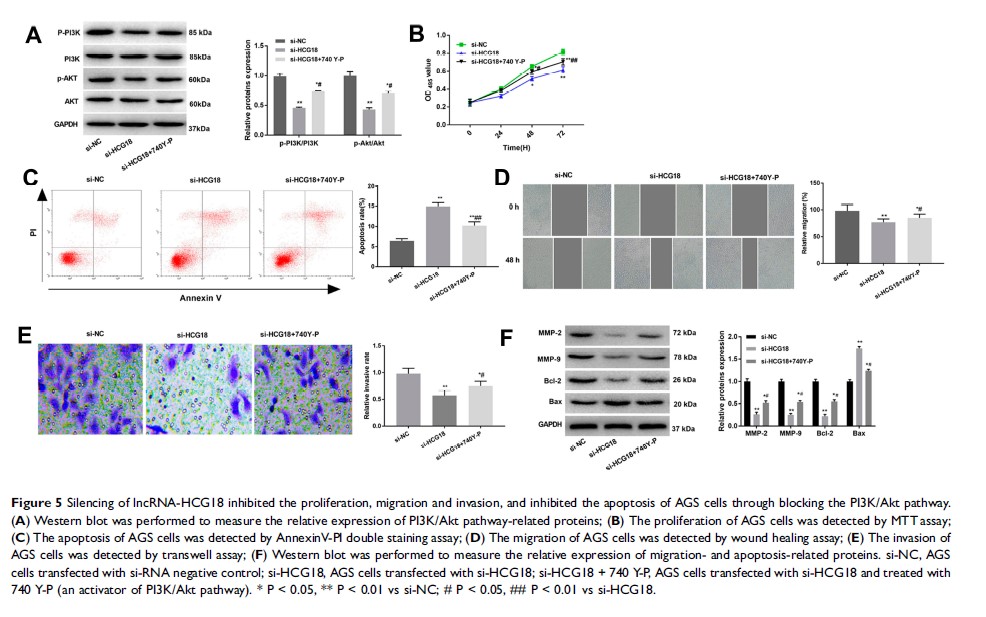
长非编码 RNA-HCG18 的沉默可通过阻断 PI3K/Akt 信号通路来遏制胃癌的肿瘤发生
Authors Ma F, An K, Li Y
Received 3 December 2019
Accepted for publication 25 February 2020
Published 18 March 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 2225—2234
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S240965
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Geoffrey Pietersz
Purpose: Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) play critical regulatory roles in the tumorigenesis of GC. This study aimed to investigate the regulatory effect and mechanism of lncRNA-HCG18 on GC.
Methods: The expression of lncRNA-HCG18 was detected in GC tissues and cell lines by qRT-PCR. LncRNA-HCG18 was silenced in AGS and MGC803 cells by the transfection of lncRNA-HCG18 siRNA (si-HCG18). MTT, transwell and Annexin V-PI double staining assay were performed to assess the proliferation, migration, invasion and apoptosis of GC cells. The expression of PI3K/Akt pathway-, apoptosis-, and migration-related proteins were detected by Western blot. An activator of PI3K/Akt pathway 740 Y-P was used to activate the PI3K/Akt pathway in AGS cells. A human tumor xenograft model was established in mice to evaluate the effects of si-HCG18 in vivo.
Results: LncRNA-HCG18 was overexpressed in GC tissues and cells. Up-regulation of lncRNA-HCG18 was positively correlated with the stage of tumor node metastasis and invasion depth. Silencing of lncRNA-HCG18 suppressed the proliferation, migration and invasion, and induced the apoptosis of GC cells. Silencing of lncRNA-HCG18 blocked the PI3K/Akt pathway. The intervention of 740Y-P reversed the anti-tumor effect of lncRNA-HCG18 on GC cells. In addition, silencing of lncRNA-HCG18 suppressed the growth of GC xenografts in mice.
Conclusion: Silencing of lncRNA-HCG18 inhibited the tumorigenesis of GC through blocking the PI3K/Akt pathway, suggesting a novel therapeutic target for GC.
Keywords: gastric cancer, lncRNA-HCG18, PI3K/Akt pathway, proliferation, migration