111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

氧化苦参碱通过减弱 RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK 通路信号来抑制外阴鳞癌细胞的增殖和迁移
Authors Wang Y, Yang S, Zhang S, Wu X
Received 13 January 2020
Accepted for publication 28 February 2020
Published 19 March 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 2057—2067
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S245696
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Seema Singh
Purpose: To evaluate the anti-tumor effects of oxymatrine in vulvar squamous cell carcinoma (VSCC) cells and to explore the underlying mechanisms.
Methods: We selected SW962 and A431 VSCC cell lines. Cell proliferation was examined using MTT assay. Cell cycle and apoptosis were detected using flow cytometry. Migration and invasion were evaluated using transwell and wound-healing assays. The relevant protein expression and signaling pathways were analyzed using Western blotting.
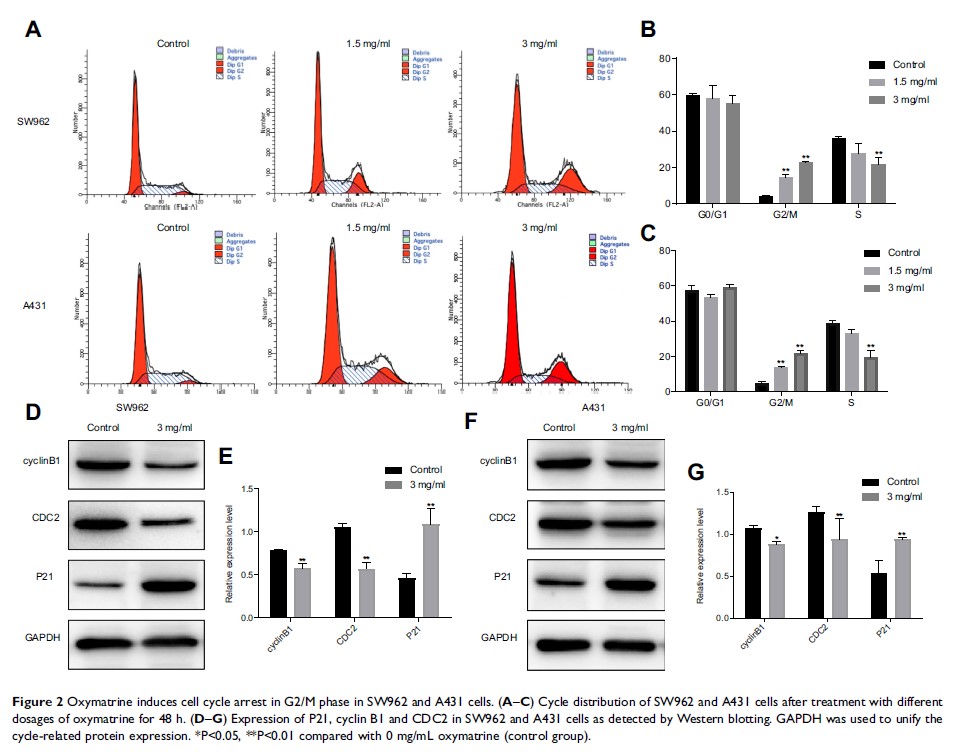
Results: Oxymatrine inhibited the proliferation of SW962 and A431 VSCC cells in a time- and dose-dependent manner. Oxymatrine induced cell cycle arrest in the G2/M phase by increasing the protein expression of P21 and decreasing levels of cyclin B1 and CDC2. Oxymatrine upregulated the expression of cleaved-caspase 3 and BAX and downregulated the expression of BCL2, which led to an increase in apoptosis. Oxymatrine also suppressed the migration and invasion of SW962 and A431 cells by reducing levels of MMP2 and MMP9. After treatment with oxymatrine or a RAS inhibitor (salirasib), expression levels of RAS, p-RAF, p-MEK, p-ERK, C-MYC, and MMP2 were reduced. When TGF-β 1 was used to stimulate SW962 and A431 cells, the expression of the above proteins increased; this increase was reversed by using oxymatrine or salirasib again.
Conclusion: Oxymatrine inhibits proliferation and migration of VSCC cells by blocking the RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK pathway.
Keywords: oxymatrine, vulvar squamous cell carcinoma, RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK