111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

KRT17 作为肿瘤启动子,通过 mTOR/S6k1 信号通路调节胰腺癌的增殖、迁移和侵袭
Authors Li D, Ni XF, Tang H, Zhang J, Zheng C, Lin J, Wang C, Sun L, Chen B
Received 20 December 2019
Accepted for publication 14 February 2020
Published 19 March 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 2087—2095
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S243129
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Antonella D'Anneo
Background: Pancreatic cancer (PC) is one of the most well-known malignancies with high mortality, but the underlying mechanism of PC remains unknown. Keratin17 (KRT17) expression has been reported in many malignancies, but its functions in PC are not clear. The aim of our study was to evaluate KRT17 expression and its potential role in PC.
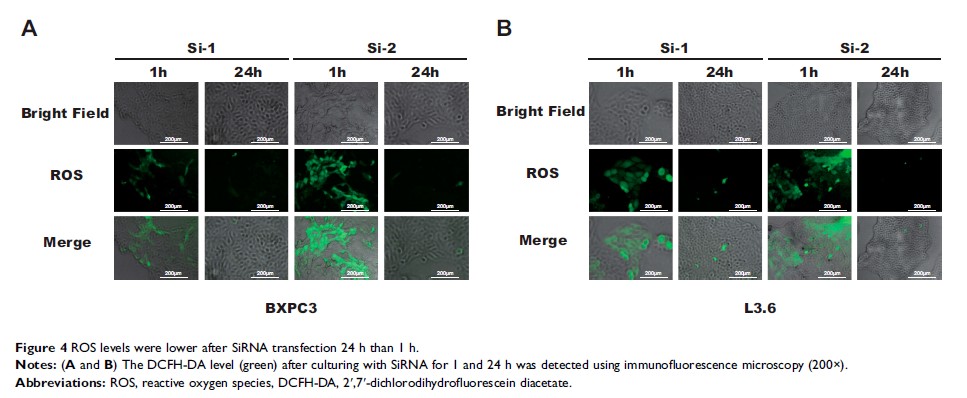
Methods: The online databases GEPIA and THPA were used to identify KRT17 expression in tissues. Quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) was used to determine KRT17 expression in cell lines. Ki67 and ROS levels were detected by immunofluorescence assay and a 2ʹ,7ʹ-dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate (DCFH-DA) probe. KRT17 downregulation was induced by the small interfering RNA (siRNA) technique. Proliferation function was evaluated by colony formation assay and RTCA. Migration and invasion were evaluated by transwell migration assay. A Western blot assay was used to detect protein levels.
Results: KRT17 was overexpressed in PC tissues compared to that in normal tissues. The results showed that Ki67 and ROS levels were decreased in pancreatic cancer cells after transfection with siKRT17. After KRT17 downregulation in PC cell lines, cell viability functions, including proliferation, migration and invasion, and mTOR/S6K1 phosphorylation levels were attenuated.
Conclusion: KRT17 knockdown significantly inhibited proliferation, migration and invasion in pancreatic cancer cells.
Keywords: KRT17, knockdown, proliferation, migration, invasion, pancreatic cancer, mTOR/S6K1