111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

Phocea 、假黄酮分子体和肠道乳杆菌:影响肥胖诱导的 2 型糖尿病进展和并发症的肠道菌群的三种潜在生物标志物
Authors Wang Y, Ouyang M, Gao X, Wang S, Fu C, Zeng J, He X
Received 2 December 2019
Accepted for publication 29 February 2020
Published 19 March 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 835—850
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DMSO.S240728
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Konstantinos Tziomalos
Purpose: The purpose of this study was to explore the difference and association between intestinal microbiota and plasma metabolomics between type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and normal group and to identify potential microbiota biomarkers that contribute the most to the difference in metabolites.
Methods: Six male ZDF model (fa/fa) rats were fed by a Purina #5008 Lab Diet (crude protein 23.5%, crude fat 6.5%) for 3 weeks and their age-matched 6 ZDF control (fa/+) rats were fed by normal rodent diet. Their stool and blood samples were collected at 12 weeks. To analyze the microbial populations in these samples, we used a 16S rRNA gene sequencing approach. Liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry (LC-MS) followed by multivariate statistical analysis was applied to the plasma metabolites profiling. Correlation analysis of them was calculated by Pearson statistical method.
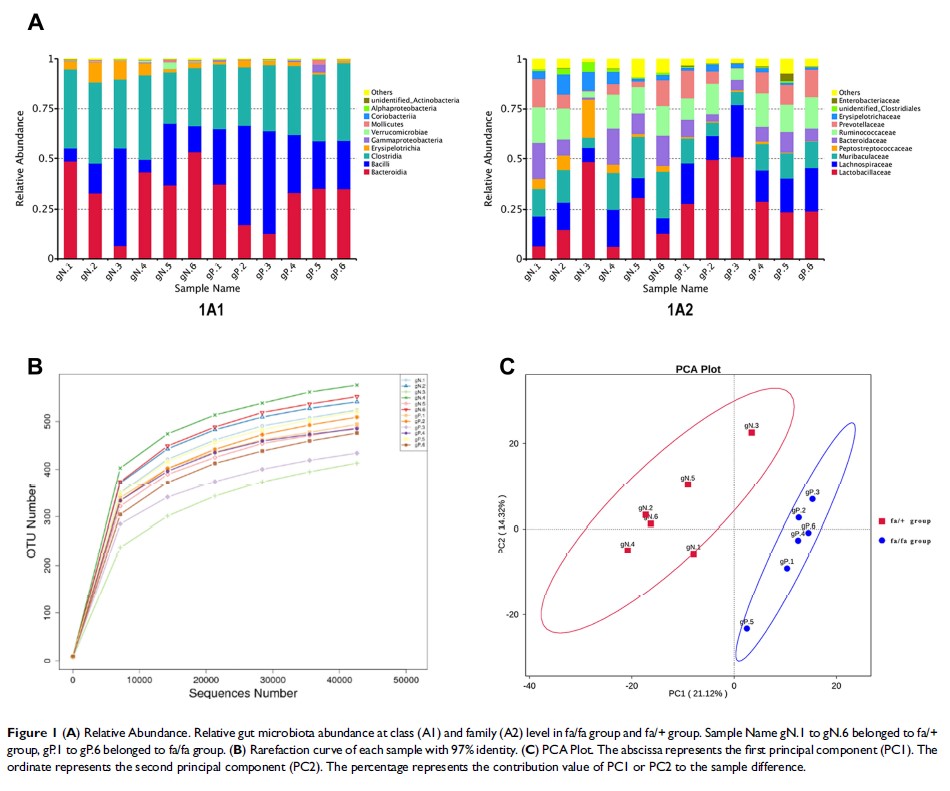
Results: Twelve potential biomarkers of intestinal microbial flora and 357 differential metabolites were found in ZDF fa/fa rats, among which there are three flora that contributed the most to the perturbation of metabolites, including genus Phocea , Pseudoflavonifractor and species Lactobacillus intestinalis .
Conclusion: Our study demonstrates the alterations of the abundance and diversity of the intestinal microbiota and the perturbation of metabolites in ZDF rats (fa/fa). We found three potential biomarkers of intestinal microbiota that may lead to perturbation in plasma metabolites. This may prompt new pathogenesis of obesity-related T2DM, but we also need to study further about the causal relationship between intestinal microbe and T2DM, so as to find the target of T2DM treatment or preventive measures.
Keywords: type 2 diabetes mellitus, Zucker diabetic fatty rats, 16S rRNA sequencing, intestinal microbiota, plasma metabolomics