111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

LncRNA FOXP4-AS1 通过调节 miR-136-5p/CBX4 轴参与宫颈癌的进展
Authors Zhao J, Yang T, Li L
Received 10 December 2019
Accepted for publication 12 February 2020
Published 19 March 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 2347—2355
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S241818
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Gaetano Romano
Introduction: Cervical cancer (CC) is a major health threat to women worldwide. Long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) has been reported to play crucial roles in regulating carcinogenesis, including CC.
Methods: In this work, levels of lncRNA forkhead box P4 antisense RNA 1 (FOXP4-AS1) in CC cell lines and normal cell lines were analyzed with quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR) method. Effects of FOXP4-AS1 on CC cellular behaviors including proliferation, migration, and invasion were explored. Bioinformatic prediction tools and luciferase activity reporter assay were conducted to explore the downstream molecules for FOXP4-AS1.
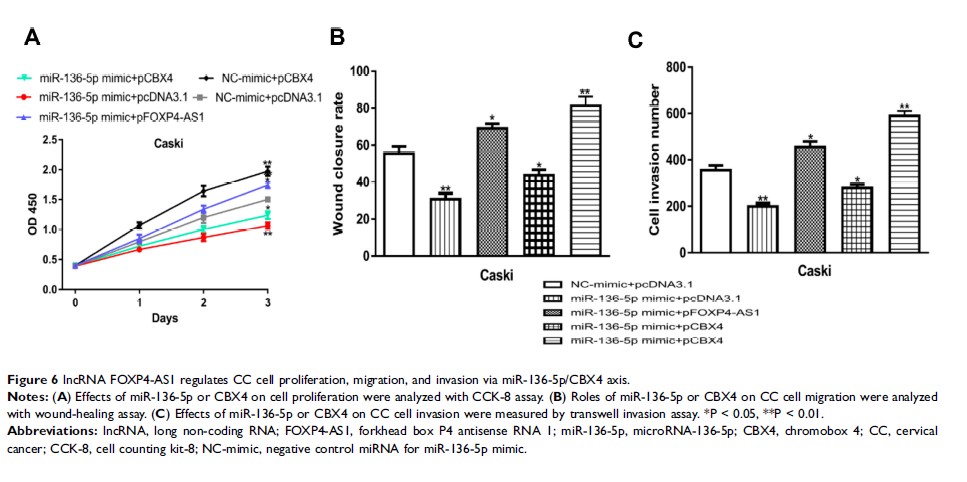
Results: We found FOXP4-AS1 expression was significantly higher in CC cell lines than in normal cell line. Functionally, force FOXP4-AS1 expression increased CC cell proliferation, migration, and invasion, while FOXP4-AS1 knockdown caused opposite effects. Mechanistically, we found FOXP4-AS1 acts as competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) for microRNA-136-5p (miR-136-5p) to regulate chromobox 4 (CBX4) expression.
Discussion: These findings indicated FOXP4-AS1 plays an oncogenic role in CC, which may provide novel therapeutic biomarker against CC.
Keywords: FOXP4-AS1, miR-136-5p, CBX4, cervical cancer