111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

芍药苷通过抑制内皮-间质转化来缓解慢性低氧/SU5416-诱导的肺动脉高压
Authors Yu M, Peng L, Liu P, Yang M, Zhou H, Ding Y, Wang J, Huang W, Tan Q, Wang Y, Xie W, Kong H, Wang H
Received 18 October 2019
Accepted for publication 25 February 2020
Published 19 March 2020 Volume 2020:14 Pages 1191—1202
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S235207
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yan Zhu
Background: Endothelial cells dysfunction is one of the hallmark pathogenic features of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). Paeoniflorin (PF) is a monoterpene glycoside with endothelial protection, vasodilation, antifibrotic, anti–inflammatory and antioxidative properties. However, the effects of PF on PAH remain unknown.
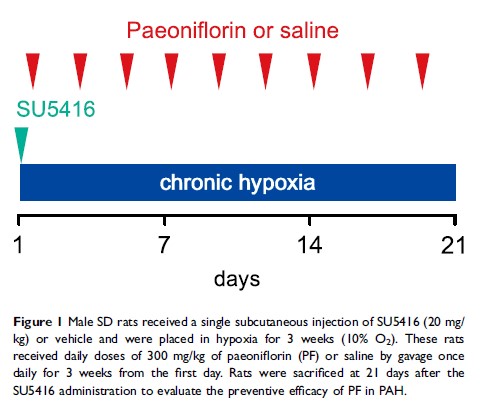
Methods: Here, we investigated the efficacy of PF in the SU5416/hypoxia (SuHx) rat model of PAH. Human pulmonary arterial endothelial cells (HPAECs) were exposed to 1% O2 with or without PF treatment.
Results: Hemodynamics analysis showed that prophylactic treatment with PF (300 mg/kg i.g. daily for 21 days) significantly inhibited chronic hypoxia/SU5416-induced elevations of right ventricular systolic pressure (RVSP) and right ventricular hypertrophy index in rats. Meanwhile, PF significantly reduced pulmonary vascular remodeling, as well as alleviated collagen deposition in lungs and right ventricles in SuHx rats. Additionally, PF inhibited SuHx–induced down-regulation of endothelial marker (vascular endothelial cadherin) and up-regulation of mesenchymal markers (fibronectin and vimentin) in lung, suggesting that PF could inhibit SuHx–induced endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EndMT) in lung. Further in vitro studies confirmed that PF treatment suppressed hypoxia-induced EndMT in HPAECs, which was abolished by the knockdown of bone morphogenetic protein receptor type 2 (BMPR2) in HPAECs.
Conclusion: Taken together, our findings suggest that PF ameliorates BMPR2 down-regulation-mediated EndMT and thereafter alleviates SuHx–induced PAH in rats.
Keywords: paeoniflorin, pulmonary arterial hypertension, endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition, BMPR2, hypoxia