111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

RAGE 的下调通过调节宫颈鳞状细胞癌中的 PI3K/AKT 信号通路抑制细胞增殖并诱导凋亡
Authors Li R, Song Y, Zhou L, Li W, Zhu X
Received 28 November 2019
Accepted for publication 11 March 2020
Published 20 March 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 2385—2397
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S240378
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Carlos E Vigil
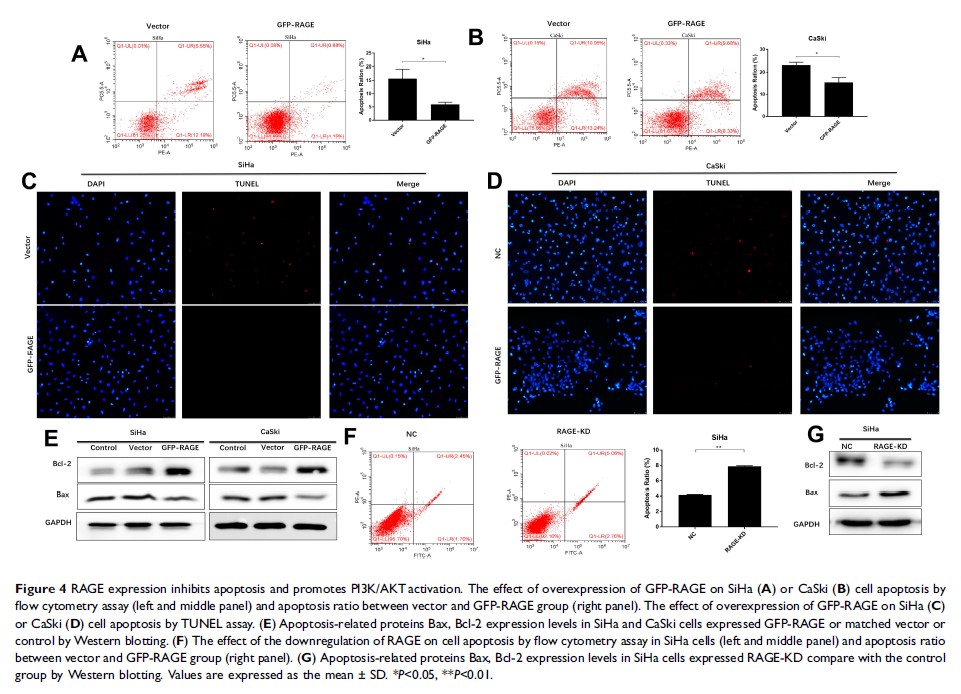
Aim: The receptor for advanced glycation endproducts (RAGE) expression has been reported to be implicated with cancer development. In this study, the role of RAGE in the regulation of cervical squamous cancer cell proliferation, apoptosis and the mechanism of RAGE involved in the biological behaviors were explored.
Methods: The RAGE expression was overexpressed or downregulated by lentivirus transfection. The effect of RAGE expression on cell proliferation was explored by CCK-8, MTT, and BrdU assay, and the effect of RAGE on tumor development was confirmed by the xenograft mouse model along with the immunohistochemistry stain of proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA). Apoptosis was investigated by flow cytometry and TUNEL assay. Western blotting was performed to investigate the expression of possible proteins, including Bax, Bcl-2, PI3K, p-PI3K, AKT, and p-AKT.
Results: Overexpression of RAGE promoted proliferation of cervical squamous cancer cell and increased PCNA expression. In the meantime, RAGE overexpression inhibited cell apoptosis along with a decrease of Bax/Bcl-2 ratio, and induction of PI3K/AKT activation. The in vivo results showed that overexpression of RAGE enhanced tumor growth. Conversely, knockdown of RAGE exhibited opposed effects on cervical cancer cells and xenograft mouse model. Furthermore, RAGE inhibitor FPS-ZM1 effectively inhibited SiHa cell viability and PCNA expression, and increased cell apoptosis and Bax/Bcl-2 ratio. Moreover, PI3K inhibitor LY294002 effectively inhibited activation of PI3K and AKT, and further repressed RAGE overexpression-induced cell proliferation and apoptosis inhibition.
Conclusion: RAGE promotes the growth ability of cervical squamous cell carcinoma by inducing PCNA expression and inhibiting cell apoptosis via inactivation of the PI3K/AKT pathway.
Keywords: RAGE, PI3K/AKT, cervical squamous cancer, proliferation, apoptosis