111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

miR-145-5p 通过靶向 KLF5 调节宫颈癌的增殖、迁移和侵袭
Authors Cao H, Pan G, Tang S, Zhong N, Liu H, Zhou H, Peng Q, Zou Y
Received 6 December 2019
Accepted for publication 25 February 2020
Published 20 March 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 2369—2376
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S241366
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Geoffrey Pietersz
Objective: Cervical carcinoma (CC) is a serious threat to women’s health and few effective therapeutic methods have been discovered. The purpose of this study is to explore the underlying mechanism of miR-145-5p in CC.
Methods: Bioinformatics methods were employed to analyze the gene expression data of CC from TCGA database. qRT-PCR was used to detect the expression of miR-145-5p and KLF5 in CC cells, and Western blot was employed for the examination of KLF5 protein level. The targeted relationship between miR-145-5p and KLF5 was verified by a dual-luciferase reporter assay. Moreover, CCK-8, wound healing assay and transwell invasion assay were used to analyze the effects of miR-145-5p overexpression or KLF5 silencing on the proliferation, migration and invasion of CC cells.
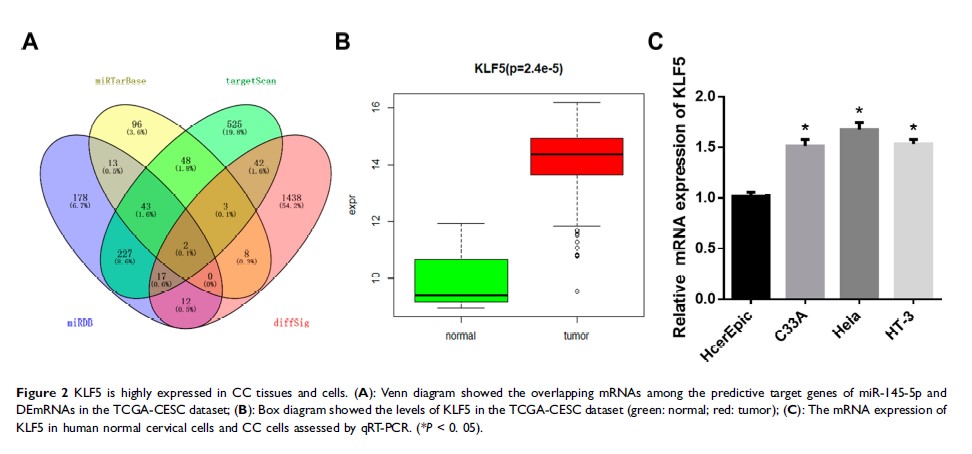
Results: miR-145-5p was shown to be down-regulated in CC tissues and cells, while KLF5 was up-regulated. miR-145-5p could bind to the complementary sequence within the wild type KLF5 3ʹUTR rather than the mutant one. In addition, miR-145-5p could effectively down-regulate KLF5, in turn inhibiting the proliferation, migration and invasion of CC cells.
Conclusion: miR-145-5p regulates the proliferation, migration and invasion of CC cells by targeting KLF5.
Keywords: cervical carcinoma, miR-145-5p, KLF5, proliferation, migration, invasion