111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

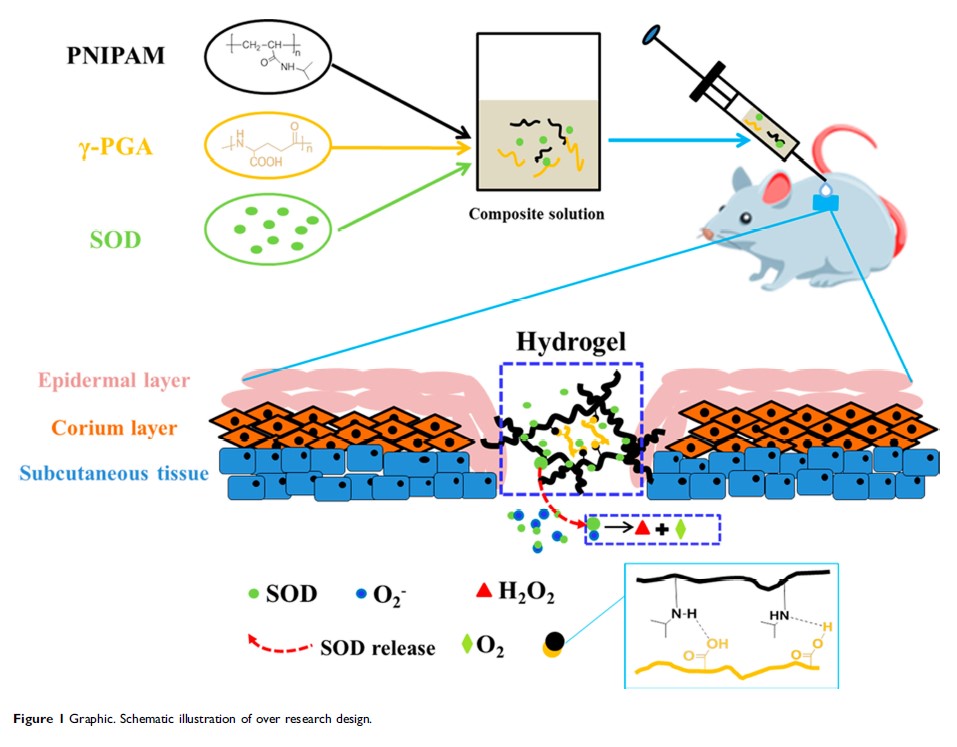
负载超氧化物歧化酶的聚(N-异丙基-丙烯酰胺)/聚(γ-谷氨酸)热敏水凝胶用于伤口敷料应用
Authors Dong Y, Zhuang H, Hao Y, Zhang L, Yang Q, Liu Y, Qi C, Wang S
Received 22 October 2019
Accepted for publication 24 February 2020
Published 20 March 2020 Volume 2020:15 Pages 1939—1950
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S235609
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Mian Wang
Introduction: Chronic trauma repair is an important issue affecting people’s healthy lives. Thermo-sensitive hydrogel is injectable in situ and can be used to treat large-area wounds. In addition, antioxidants play important roles in promoting wound repair.
Methods: The purpose of this research was to prepare a novel thermo-sensitive hydrogel-poly(N-isopropyl-acrylamide)/poly(γ-glutamic acid) (PP) loaded with superoxide dismutase (SOD) to improve the effect for trauma treatment. The micromorphology of the hydrogel was observed by scanning electron microscope and the physical properties were measured. The biocompatibility of hydrogel was evaluated by MTT experiment, and the effect of hydrogel on skin wound healing was evaluated by in vivo histological staining.
Results: Gelling behavior and differential scanning calorimeter outcomes showed that the PP hydrogels possessed thermo-sensitivity at physiological temperature and the phase transformation temperature was 28.2°C. The high swelling rate and good water retention were conducive to wound healing. The activity of SOD in vitro was up to 85% at 10 h, which was advantageous to eliminate the superoxide anion. MTT assay revealed that this hydrogel possessed good biocompatibility. Dressings of PP loaded with SOD (SOD-PP) had a higher wound closure rate than other treatments in vivo in diabetic rat model.
Discussion: The SOD-PP thermo-sensitive hydrogels can effectively promote wound healing and have good application prospects for wound repair.
Keywords: thermo-sensitive hydrogels, wound dressing, superoxide dismutase, poly(γ-glutamic acid)