111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

2002 年营养风险筛查和微型营养评定简化量表对中国住院老年患者死亡率的预测价值
Authors Zhang X, Zhang X, Zhu Y, Tao J, Zhang Z, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Ke Y, Ren C, Xu J
Received 6 January 2020
Accepted for publication 6 March 2020
Published 20 March 2020 Volume 2020:15 Pages 441—449
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CIA.S244910
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Zhi-Ying Wu
Background and Aim: The presence of malnutrition in hospitalized geriatric patients is associated with an increased risk of mortality. This study aimed to examine the performance of Nutritional Risk Screening 2002 (NRS2002) and Mini Nutritional Assessment Short Form (MNA-SF) in predicting mortality for hospitalized geriatric patients in China.
Methods: A prospective analysis was performed in 536 hospitalized geriatric patients aged ≥ 65 years. Nutrition status was assessed using the MNA-SF and NRS2002 scales within 24 hrs of admission. Anthropometric measures and biochemical parameters were carried out for each patient. Patients were follow-up for up to 2.5 years.
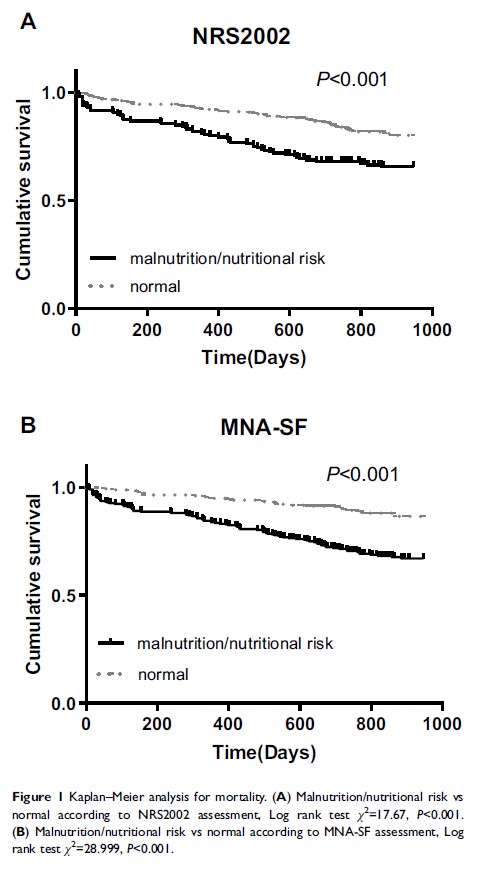
Results: At baseline, 161 (30.04%) patients had malnutrition/nutritional risk according to NRS2002 assessment. According to MNA-SF, 284 (52.99%) patients had malnutrition/nutritional risk. Malnutrition/nutritional risk patients had lower anthropometric and biochemical parameters (P < 0.05). NRS2002 and MNA-SF had a strong correlation with classical nutritional markers (P < 0.05). NRS2002 versus MNA-SF showed moderate agreement (kappa=0.493, P < 0.001). During a median follow-up time of 795 days (range 10– 947 days), 118 (22%) participants died. The Kaplan–Meier curve demonstrated that malnutrition/nutritional risk patients according to NRS2002 or MNA-SF assessment had a higher risk of mortality than the normal nutrition patients (χ 2=17.67, P < 0.001; χ 2=28.999, P < 0.001, respectively). From the components of the Cox regression multivariate models, only the NRS2002 score was an independent risk factor influencing the mortality.
Conclusion: Both NRS2002 and MNA-SF scores could predict mortality in Chinese hospitalized geriatric patients. But only NRS2002 score was the independent predictor for mortality.
Keywords: NRS2002, MNA-SF, elderly, nutritional screening, malnutrition