111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

本文章已被撤回:长非编码 RNA CASC19 会促进 microRNA-532 海绵化,并通过增加 ETS1 表达促进肾透明细胞癌的致癌性
Authors Luo Y, Liu F, Yan C, Qu W, Zhu L, Guo Z, Zhou F, Zhang W
Received 15 December 2019
Accepted for publication 27 February 2020
Published 24 March 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 2195—2207
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S242472
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Eileen O'Reilly
***本文章已被撤回***
Purpose: The long non-coding RNA cancer susceptibility 19 (CASC19 ) is recognized as an important regulator in gastric cancer, colorectal cancer, and non-small cell lung cancer. Nevertheless, to the best of our knowledge, the expression status and detailed roles of CASC19 in clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) have not been elucidated. Hence, we aimed to determine CASC19 expression in ccRCC and investigate its roles in ccRCC oncogenicity. The molecular mechanisms underlying CASC19 functions in ccRCC were also determined.
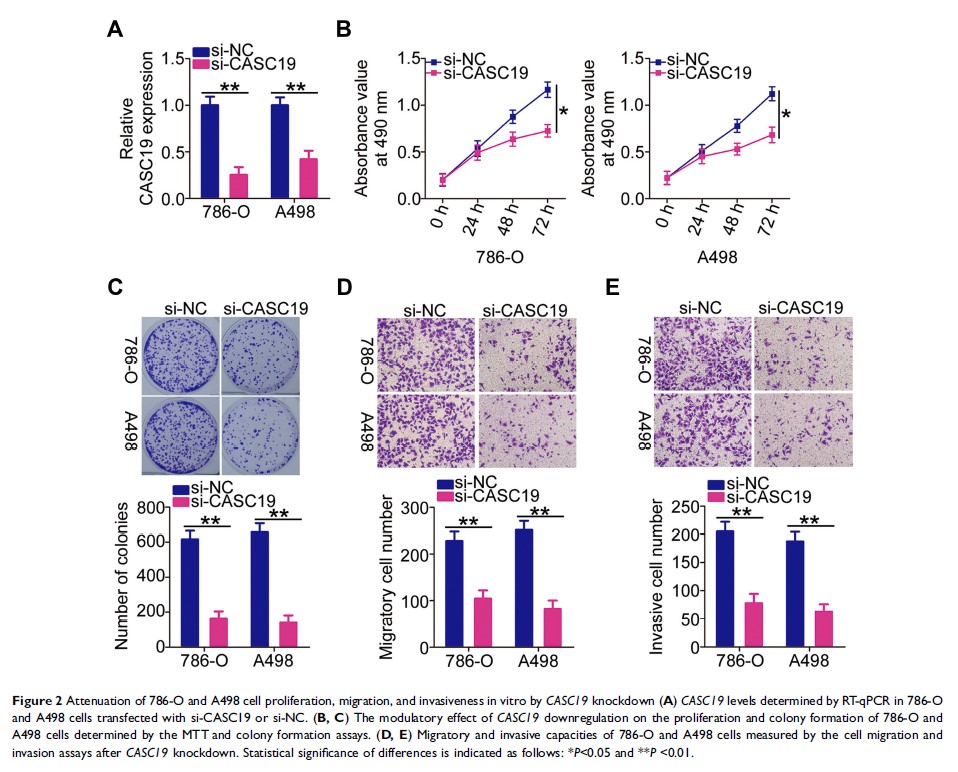
Methods: CASC19 expression was measured by using reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction. The effects of CASC19 on ccRCC cell proliferation, colony formation, migration, and invasiveness in vitro, as well as on tumor growth in vivo, were examined by the MTT assay, colony formation assay, cell migration and invasiveness assays, and tumor xenograft in nude nice, respectively.
Results: CASC19 was overexpressed in ccRCC tissues and cell lines. High expression of CASC19 was closely associated with unfavorable clinicopathological parameters and predicted negative clinical outcomes in patients with ccRCC. Knockdown of CASC19 decreased ccRCC cell proliferation, colony formation, migration, and invasiveness, as well as attenuated tumor growth in vivo. Mechanistically, CASC19 functioned as a competing endogenous RNA and upregulated the expression of ETS proto-oncogene 1 (ETS1) through sponging microRNA-532 (miR-532). Furthermore, rescue assays revealed that inhibiting miR-532 or restoring ETS1 expression partially abolished the impacts of CASC19 knockdown on ccRCC cells.
Conclusion: The CASC19/miR-532/ETS1 regulatory pathway is crucial for the malignant manifestations of ccRCC, which makes it an attractive target for potential treatments of ccRCC.
Keywords: cancer, MTT assay, cell migration, invasiveness, xenograft, knockdown