111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

CK19 通过影响 Wnt/β-连环蛋白信号通路促进卵巢癌发展
Authors Lu Q, Qu H, Lou T, Liu C, Zhang Z
Received 18 December 2019
Accepted for publication 12 March 2020
Published 24 March 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 2421—2431
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S242778
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Carlos E Vigil
Background: Epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC) is the most common type of ovarian cancer and is the most lethal gynecologic malignancy. Cytokeratin 19 (CK19) is a small type I cytokeratin. The aim of this study is to explore the functional role of CK19 and its underlying mechanism in EOC.
Methods: The expression levels of CK19 in EOC tissues were identified by Western blotting and RT-PCR assay. Transwell assay and CCK-8 proliferation assay were used to assess the invasion, migration and proliferation abilities of overexpressed or knockdown CK19 of ovarian cancer cells. We also detected the related genes of Wnt/β-catenin signal pathway, including β-catenin, TCF7, LEF1, c-MYC and cyclin D1 in the transfected ovarian cancer cells by Western blotting and RT-PCR assay.
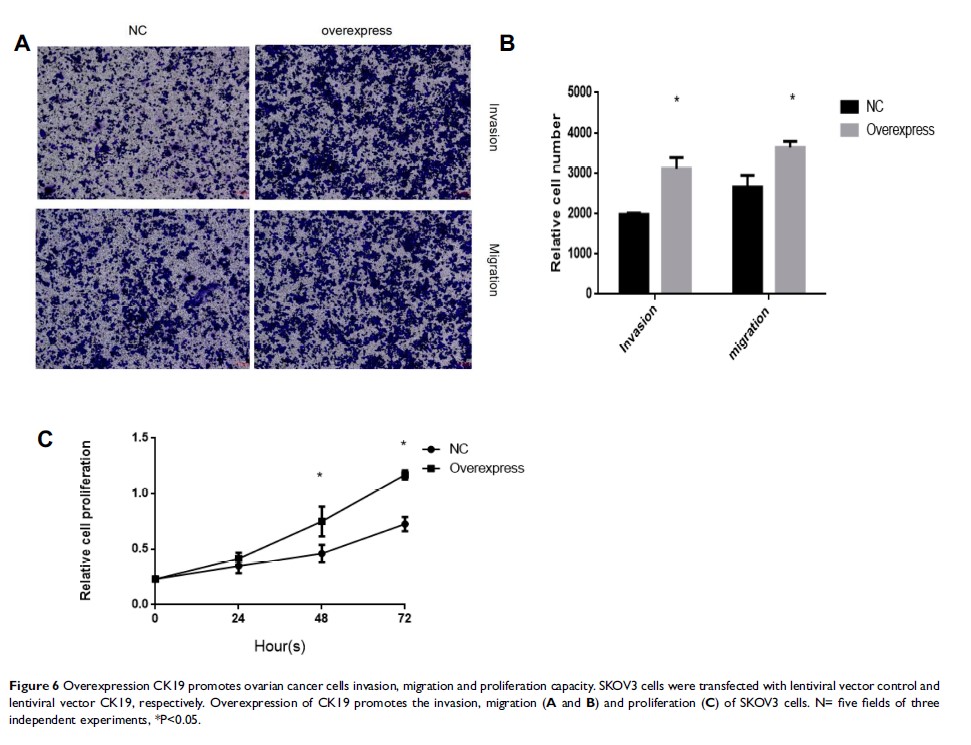
Results: The results demonstrated that CK19 was upregulated in EOC tissue. CK19 was verified to promote the invasion, proliferation and migration of ovarian cancer cells. Additionally, CK19 activates the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway by upregulated β-catenin, TCF7, LEF1, c-MYC and cyclin D1.
Conclusions: In summary, this is the first study to investigate the role of CK19 in EOC. These findings provide a potential new therapeutic target for the clinical diagnosis and treatment of ovarian cancer.
Keywords: CK19, Wnt/β-catenin, ovarian cancer, SKOV3