111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

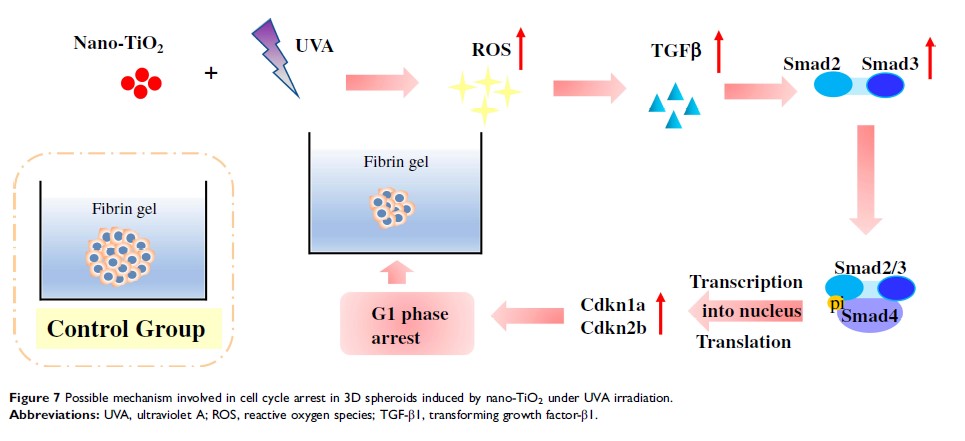
3D 椭球模型中,在 UVA 辐射下并经二氧化钛纳米粒子诱导,TGF-β 和 ROS 参与 G1 细胞周期阻滞
Authors Ren Y, Geng R, Lu Q, Tan X, Rao R, Zhou H, Yang X, Liu W
Received 11 November 2019
Accepted for publication 21 February 2020
Published 24 March 2020 Volume 2020:15 Pages 1997—2010
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S238145
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Background: As one of the most widely produced engineered nanomaterials, titanium dioxide nanoparticles (nano-TiO2) are used in biomedicine and healthcare products, and as implant scaffolds; therefore, the toxic mechanism of nano-TiO2 has been extensively investigated with a view to guiding application. Three-dimensional (3D) spheroid models can simplify the complex physiological environment and mimic the in vivo architecture of tissues, which is optimal for the assessment of nano-TiO2 toxicity under ultraviolet A (UVA) irradiation.
Methods and Results: In the present study, the toxicity of nano-TiO2 under UVA irradiation was investigated in 3D H22 spheroids cultured in fibrin gels. A significant reduction of approximately 25% in spheroid diameter was observed following treatment with 100 μg/mL nano-TiO2 under UVA irradiation after seven days of culture. Nano-TiO2 under UVA irradiation triggered the initiation of the TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway, increasing the expression levels of TGF-β 1, Smad3, Cdkn1a, and Cdkn2b at both the mRNA and protein level, which resulted in cell cycle arrest in the G1 phase. In addition, nano-TiO2 under UVA irradiation also triggered the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which were shown to be involved in cell cycle regulation and the induction of TGF-β 1 expression.
Conclusion: Nano-TiO2 under UVA irradiation induced cell cycle arrest in the G1 phase and the formation of smaller spheroids, which were associated with TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway activation and ROS generation. These results reveal the toxic mechanism of nano-TiO2 under UVA irradiation, providing the possibility for 3D spheroid models to be used in nanotoxicology studies.
Keywords: nano-TiO2, cell cycle arrest, TGF-β signaling pathway, reactive oxygen species, 3D spheroid culture