111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

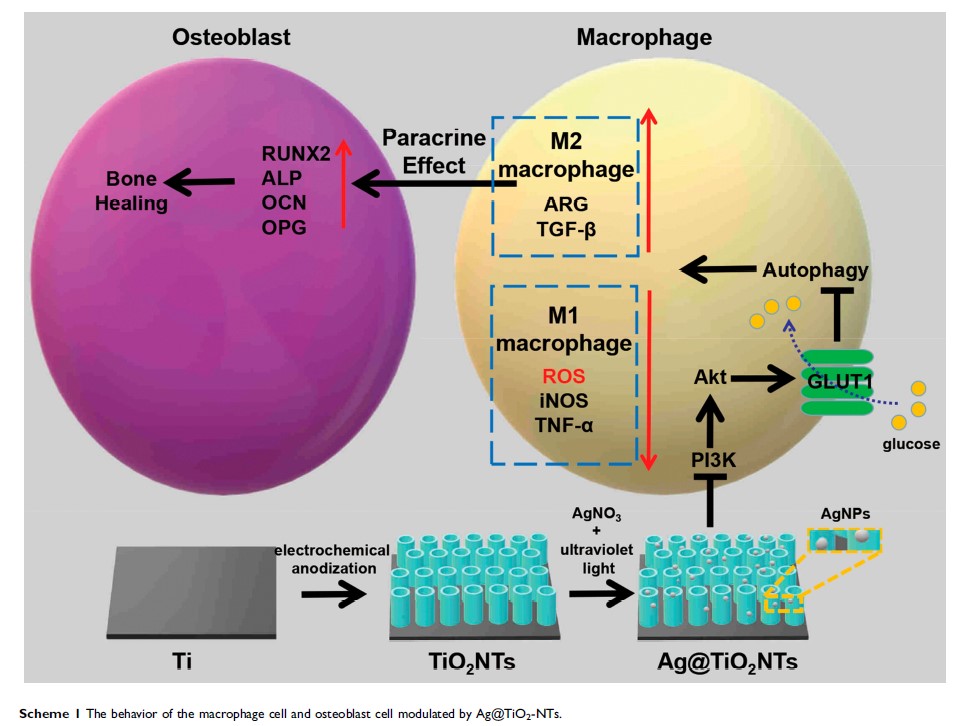
通过调节 GLUT1 和自噬,经由 M2 型巨噬细胞极化可改善超低剂量的负载银纳米颗粒的 TiO2 纳米管的免疫调控
Authors Chen Y, Guan M, Ren R, Gao C, Cheng H, Li Y, Gao B, Wei Y, Fu J, Sun J, Xiong W
Received 19 December 2019
Accepted for publication 10 March 2020
Published 24 March 2020 Volume 2020:15 Pages 2011—2026
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S242919
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Mian Wang
Introduction: The bone regeneration of endosseous implanted biomaterials is often impaired by the host immune response, especially macrophage-related inflammation which plays an important role in the bone healing process. Thus, it is a promising strategy to design an osteo-immunomodulatory biomaterial to take advantage of the macrophage-related immune response and improve the osseointegration performance of the implant.
Methods: In this study, we developed an antibacterial silver nanoparticle-loaded TiO2 nanotubes (Ag@TiO2-NTs) using an electrochemical anodization method to make the surface modification and investigated the influences of Ag@TiO2-NTs on the macrophage polarization, osteo-immune microenvironment as well as its potential molecular mechanisms in vitro and in vivo.
Results: The results showed that Ag@TiO2-NTs with controlled releasing of ultra-low-dose Ag+ ions had the excellent ability to induce the macrophage polarization towards the M2 phenotype and create a suitable osteo-immune microenvironment in vitro, via inhibiting PI3K/Akt, suppressing the downstream effector GLUT1, and activating autophagy. Moreover, Ag@TiO2-NTs surface could improve bone formation, suppress inflammation, and promote osteo-immune microenvironment compared to the TiO2-NTs and polished Ti surfaces in vivo. These findings suggested that Ag@TiO2-NTs with controlled releasing of ultra-low-dose Ag+ ions could not only inhibit the inflammation process but also promote the bone healing by inducing healing-associated M2 polarization.
Discussion: Using this surface modification strategy to modulate the macrophage-related immune response, rather than prevent the host response, maybe a promising strategy for implant surgeries in the future.
Keywords: silver nanoparticle, TiO2 nanotubes, immune response, glucose transport, autophagy