111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

自微乳化药物递送系统可改善阿魏酸的口服递送和催眠功效
Authors Liu CS, Chen L, Hu YN, Dai JL, Ma B, Tang QF, Tan XM
Received 29 November 2019
Accepted for publication 10 March 2020
Published 25 March 2020 Volume 2020:15 Pages 2059—2070
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S240449
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Mian Wang
Purpose: Ferulic acid (FA) is a natural compound which is used to treat insomnia. However, its use is limited because of its poor oral bioavailability caused by extremely rapid elimination. The current study aimed to develop a self-microemulsifying drug delivery system (SMEDDS) to improve the oral delivery of FA and to enhance its hypnotic efficacy.
Methods: FA-SMEDDS was prepared, and its morphology and storage stability were characterized. The formulation was also subjected to pharmacokinetic and tissue distribution studies in rats. The hypnotic efficacy of FA-SMEDDS was evaluated in p -chlorophenylalanine-induced insomnia mice.
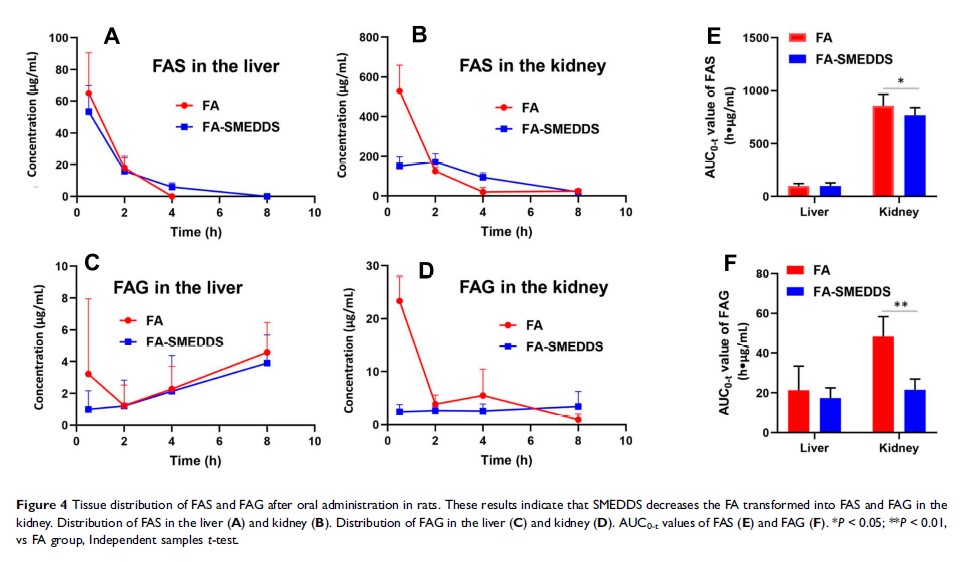
Results: FA-loaded SMEDDS exhibited a small droplet size (15.24 nm) and good stability. Oral administration of FA-SMEDDS yielded relative bioavailability of 185.96%. In the kidney, SMEDDS decreased the distribution percentage of FA from 76.1% to 59.4% and significantly reduced its metabolic conversion, indicating a reduction in renal elimination. Interestingly, FA-SMEDDS showed a higher distribution in the brain and enhanced serotonin levels in the brain, which extended the sleep time by 2-fold in insomnia mice.
Conclusion: This is the first study to show that FA-loaded SMEDDS decreased renal elimination, enhanced oral bioavailability, increased brain distribution, and improved hypnotic efficacy. Thus, we have demonstrated that SMEDDS is a promising carrier which can be employed to improve the oral delivery of FA and facilitate product development for the therapy of insomnia.
Keywords: insomnia, ferulic acid, oral administration, pharmacokinetics, SMEDDS