111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

长非编码 RNA FGD5-AS1 充当在 microRNA-383 上的竞争性内源 RNA,通过增加 SP1 表达来增强食管鳞状细胞癌的恶性特征
Authors Gao J, Zhang Z, Su H, Zong L, Li Y
Received 30 October 2019
Accepted for publication 18 February 2020
Published 26 March 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 2265—2278
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S236576
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Kenan Onel
Purpose: Previous studies have identified the important roles of a long noncoding RNA called FGD5 antisense RNA 1 (FGD5-AS1 ) in several types of human cancer. Nonetheless, to our knowledge, the expression and functions of FGD5-AS1 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) have not been clarified. In this study, we aimed to determine the expression status of long noncoding RNA FGD5-AS1 in ESCC, determine its participation in ESCC progression, and uncover the underlying mechanisms.
Methods: ESCC tissue samples and paired normal adjacent tissues were collected to quantify FGD5-AS1 expression by reverse-transcription quantitative PCR. The effects of FGD5-AS1 on ESCC cell proliferation, apoptosis, migration, and invasion in vitro as well as tumor growth in vivo were studied using a Cell Counting Kit-8 assay, flow cytometry, Transwell migration and invasion assays, and an in vivo tumor xenograft experiment.
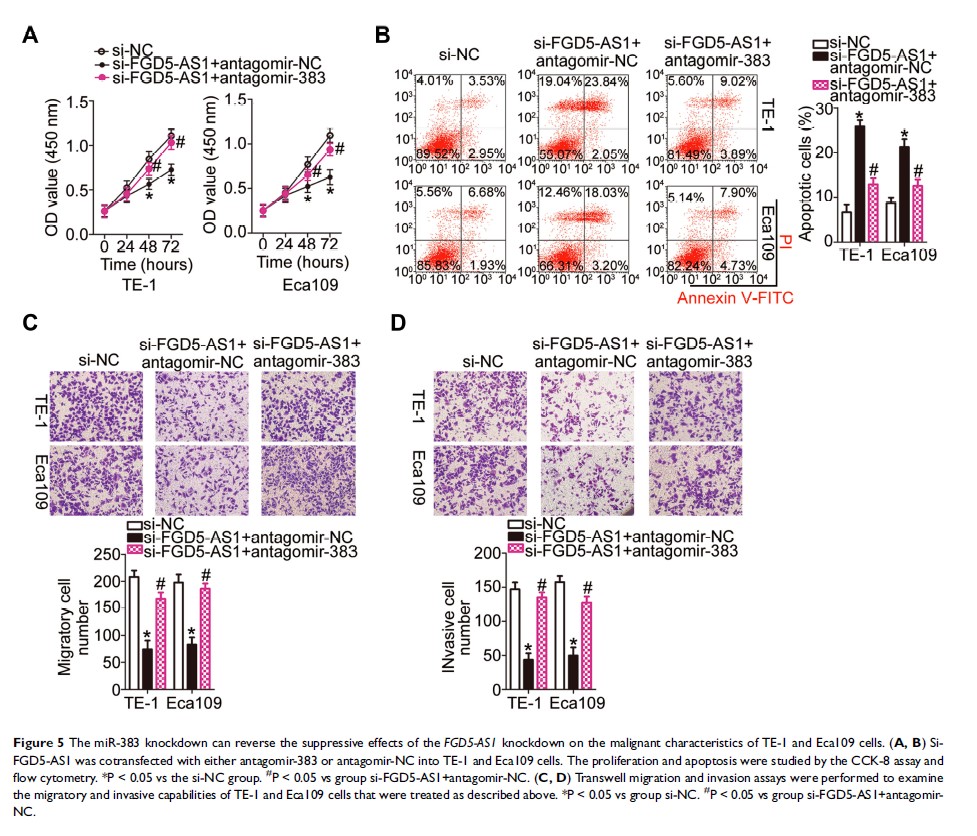
Results: FGD5-AS1 was found to be aberrantly upregulated in both ESCC tumors and cell lines compared to the control groups. Increased FGD5-AS1 expression manifested a close association with tumor size, TNM stage, and lymph node metastasis in patients with ESCC. Overall survival of patients with ESCC was shorter in the FGD5-AS1 high-expression group than in the FGD5-AS1 low-expression group. An FGD5-AS1 knockdown markedly attenuated ESCC cell proliferation, migration, and invasion and promoted apoptosis in vitro as well as slowed tumor growth in vivo. Mechanism investigation revealed that FGD5-AS1 can increase SP1 expression by sponging microRNA-383 (miR-383), thus functioning as a competing endogenous RNA. An miR-383 knockdown and recovery of SP1 expression attenuated the inhibition of the malignant characteristics of ESCC cells by the FGD5-AS1 knockdown.
Conclusion: Thus, FGD5-AS1 enhances the aggressive phenotype of ESCC cells in vitro and in vivo via the miR-383–SP1 axis, which may represent a novel target for ESCC therapy.
Keywords: esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, FGD5 antisense RNA 1, microRNA-383