111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

IL-10 与 NGAL 结合对慢性阻塞性肺疾病急性加重(AECOPD)合并急性肾损伤(AKI)患者具有诊断价值
Authors Wei B, Tian T, Liu YG
Received 10 January 2020
Accepted for publication 15 March 2020
Published 26 March 2020 Volume 2020:15 Pages 637—644
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/COPD.S245541
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Chunxue Bai
Background: In patients with acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (AECOPD) complicated by acute kidney injury (AKI) has an acute onset and seriously affects the prognosis of patients. The inflammatory factors are still in doubt in the diagnosis of AECOPD with AKI.
Material and Methods: This study is a retrospective study. By collecting the plasma concentrations of inflammatory factors IFN-γ, IL-2, IL-4, IL-10, IL-17, and NGAL in patients with AECOPD group, AECOPD plus AKI group, and control group. The expression level of each factor among the three different groups was analyzed, and the correlation of each factor was analyzed. The diagnostic value of each factor in patients with AECOPD combined with AKI was tested.
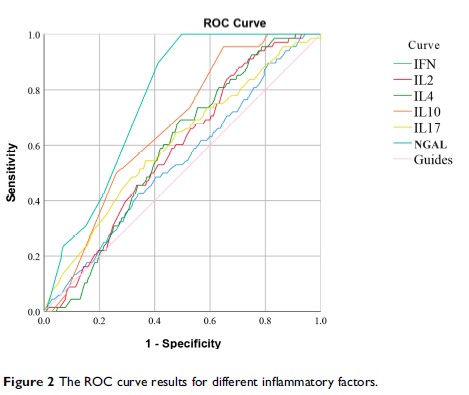
Results: A total of 245 cases of AECOPD, 69 cases of AECOPD with AKI, and 50 healthy control group were included in this study. IFN-γ and IL-4 were differentially expressed among the three groups (P < 0.001). However, there was no difference between the AECOPD group and the AECOPD + AKI group (P = 0.153, and 0.070, respectively). The expression of IL-2, IL-10, IL-17, and NGAL in the three groups were different, and there are statistical differences in pairwise comparisons. (all P values are < 0.001). The univariate analysis showed that NGAL and IL-10 with the best correlation (r = 0.696). The ROC curve shows that IL-10 and NGAL have better diagnostic value for AECOPD with AKI.
Conclusion: The inflammatory factor IL-10 combined with NGAL has a better diagnostic value for AECOPD with AKI.
Keywords: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, acute exacerbation, acute kidney injury, inflammatory factors, diagnosis