111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

MiR-802 通过靶向 RAN 抑制大肠癌细胞的生存力、迁移和侵袭
Authors Feng H, Liu L, Xu L, Wang H, Hua Q, He P
Received 19 September 2019
Accepted for publication 21 February 2020
Published 26 March 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 2291—2300
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S231709
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Nakshatri
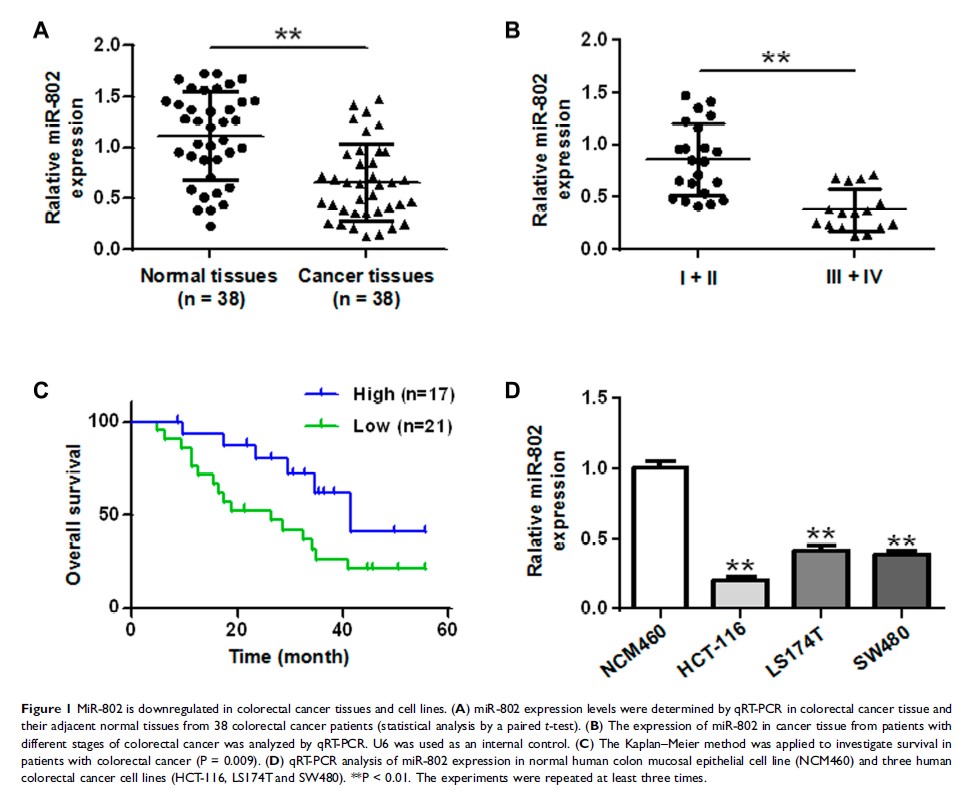
Purpose: Colorectal cancer is one of the most malignant tumors in the world, and the incidence is increasing every year. MicroRNAs (miRNA) are small non-coding RNAs that are involved in a variety of physiological or pathological processes. Abnormal expression of microRNA-802 (miR-802) has been demonstrated in various types of cancer. However, the expression and biological role of miR-802 in human colorectal cancer remain largely unknown.
Methods: Here, we used quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) to measure miR-802 expression levels in colorectal cancer tissues and cell lines. Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) was used to assess the effect of miR-802 on colorectal cancer cell viability. Migration and invasion assays were performed to determine the effect of miR-802 on metastasis of colon tumor cells by transwell analysis. Luciferase activity assays were used to confirm the target of miR-802.
Results: The results show that miR-802 is significantly downregulated in colorectal cancer tissues and cell lines. Overexpression of miR-802 profoundly inhibited viability, migration and invasion of colorectal cancer cells. In addition, we have newly discovered that the Ras-associated nucleus (RAN) is a direct target of miR-802 which could reverse the effects induced by miR-802 overexpression in colorectal cancer cells.
Conclusion: In conclusion, our study shows that miR-802 is downregulated in colorectal cancer, and overexpression of miR-802 inhibits colorectal cancer cell viability, migration and invasion by directly targeting RAN.
Keywords: miR-802, colorectal cancer, RAN, viability, migration, invasion