111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

成纤维细胞活化蛋白(FAP)过表达通过下调二肽基肽酶 9(DPP9)诱导口腔鳞状细胞癌上皮-间质转化(EMT)
Authors Wu Q, Zhao M, Huang G, Zheng Z, Chen Y, Zeng W, Lv X
Received 23 December 2019
Accepted for publication 2 March 2020
Published 27 March 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 2599—2611
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S243417
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Nicola Silvestris
Purpose: Fibroblast activation protein (FAP) acts as a tumor promoter via epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) in human oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC). The present study was designed to investigate the FAP targeting proteins and explore the precise mechanism by which FAP promotes EMT in OSCC.
Patients and Methods: Proteins interacting with FAP were found and filtered by immunoprecipitation-mass spectrometry (IP-MS). Both DPP9 protein and mRNA were examined in 90 paired OSCC samples and matched normal tissue. DPP9 knockdown was conducted to determine its function in OSCC in vitro and in vivo.
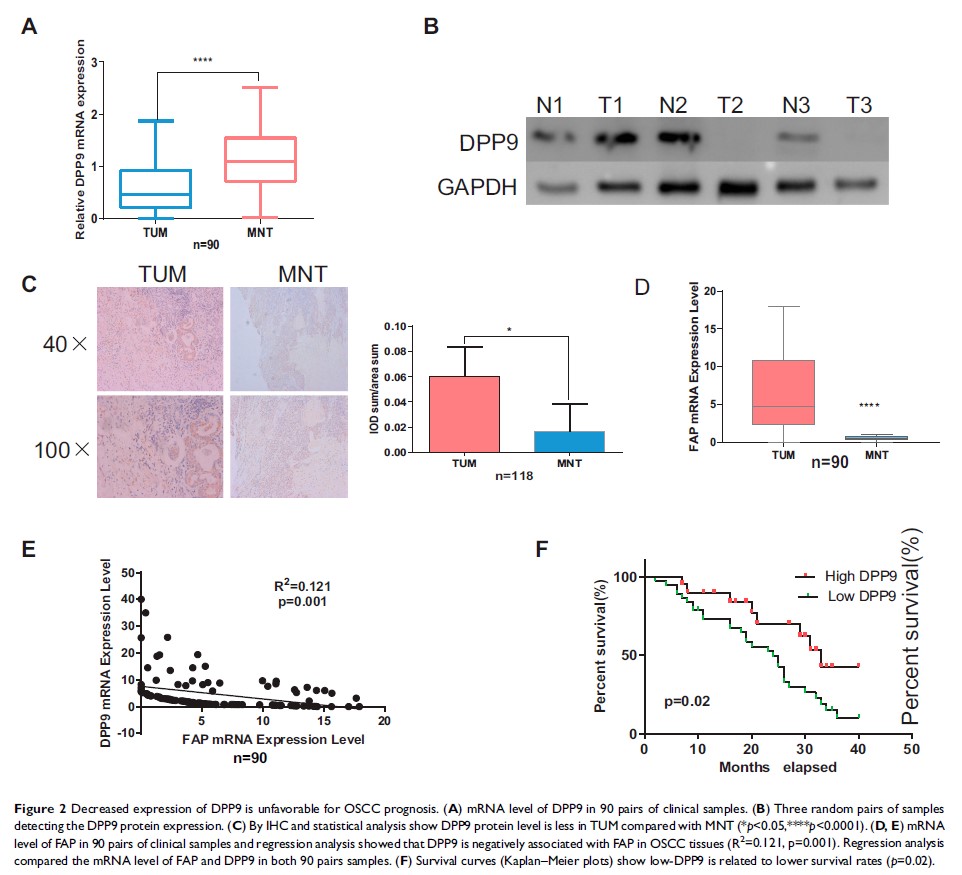
Results: Dipeptidyl peptidase 9 (DPP9) was identified as interacting with FAP intracellularly by IP-MS. The levels of both DPP9 protein and mRNA were down-regulated in OSCC tissue. Lower DPP9 expression was correlated with unfavorable survival rates of OSCC patients. DPP9 knockdown accelerates the proliferation of OSCC cells in vitro and in vivo. Overexpression of FAP leads to a reduction in DPP9 expression. Likewise, DPP9 overexpression reverses the proliferation, migration, invasion and EMT induced by FAP during OSCC.
Conclusion: Our study finds that FAP promotes EMT of OSCC by down-regulating DPP9 in a non-enzymatic manner. FAP-DPP9 pathway could be a potential therapeutic target of OSCC.
Keywords: FAP, DPP9, EMT, OSCC, oral cancer