111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

肝细胞癌 GPC3 纳米抗体的制备与表征
Authors Xia L, Teng Q, Chen Q, Zhang F
Received 17 October 2019
Accepted for publication 10 March 2020
Published 30 March 2020 Volume 2020:15 Pages 2197—2205
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S235058
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Mian Wang
Background: Glypican-3 (GPC3) is a newly identified target molecule for the early diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), while targeted inhibition of GPC3 signaling may help to control the proliferation and metastasis of HCC cells. The purpose of this study was to prepare the anti-GPC3 nanobody and to investigate the affinity of the anti-GPC3 nanobodies in vitro and the anticancer effects on hepatocellular carcinoma in vivo.
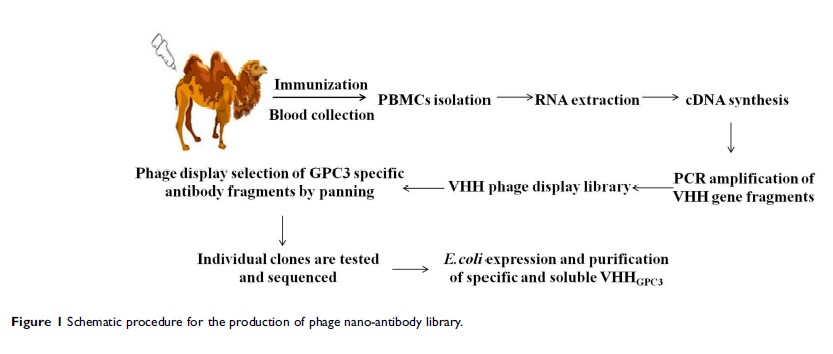
Methods: To screen for unknown anti-GPC3 antibodies, we constructed an antibody phage display library. After three rounds of panning, positive phage clones were identified by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Further, the nanobody fusion protein was expressed in E. coli BL21 cells and purified by affinity chromatography. Competitive ELISA and flow cytometry were conducted to confirm the affinity of the anti-GPC3 nanobodies in vitro. The antitumor effects of VHHGPC3 were assessed in vivo.
Results: The results showed that the nanobody VHHGPC3 had specific high-affinity binding to His-GPC3 antigen. Moreover, VHHGPC3 exhibited specific binding to commercial human GPC3 and recognized the surface GPC3 protein of the hepatoma cell line HepG2. Importantly, in vivo study showed that GPC3 nanobody suppresses the growth of HepG2 and improves the survival rate of tumor mice.
Discussion: In summary, our new anti-GPC3 nanobody suggests a strong application potential for targeted therapy of liver cancer.
Keywords: GPC3, phage display library, selection, nanobody