111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

三角叶薯蓣皂苷可改善与自噬和炎症调节相关的脑缺血/再灌注损伤
Authors Zhang Y, Tian Z, Wan H, Liu W, Kong F, Ma G
Received 20 August 2019
Accepted for publication 6 January 2020
Published 31 March 2020 Volume 2020:16 Pages 871—879
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S227988
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yu-Ping Ning
Introduction: Deltonin, an active component extracted from Dioscorea zingiberensis C.H. WRIGHT, was widely utilized in traditional Chinese medicines. It has been shown to have anti-cancer functions such as colon cancer, breast cancer, and head and neck squamous carcinoma. Herein, we will investigate the role of deltonin in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injuries.
Methods: Ly294002 and anisomycin were used as inhibitors to monitor the effects of deltonin. Middle cerebral artery occlusion I/R model was constructed. Infarct volumes, neurological deficits and brain water contents were evaluated under different conditions. Rotarod test, ELISA, and Western blotting were carried to investigate the effects in vitro.
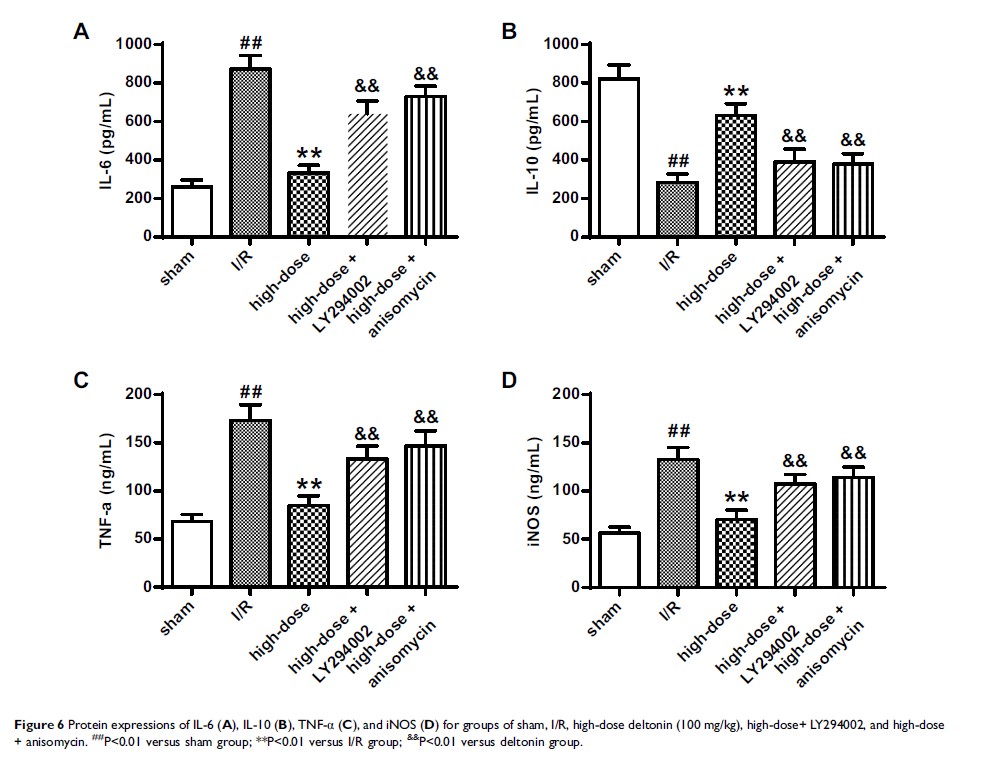
Results: We found that deltonin in ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) rats greatly enhanced brain damages as well as neurological functions through up-regulating p-Akt and p-mTOR as well as inhibiting the expressions of LC3-II/LC3-I, Beclin-1, IL-1, TLR4, and p-p38. Deltonin exerted neuroprotection effect through relieving autophagy activity by regulating PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling. Deltonin suppressed inflammation reactions through modulation TLR4/p38/MAPK signaling as well.
Conclusion: Overall, our data suggested that deltonin could suppress ischemic brain injury by regulating autophagy and inflammation during I/R. Deltonin can be a potential therapeutic method for patient with I/R.
Keywords: deltonin, cerebral I/R, MCAO/R, autophagy, inflammation