111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

肠道菌群通过神经内分泌-免疫-线粒体信号通路调节大鼠的抑郁样行为
Authors Liu S, Guo R, Liu F, Yuan Q, Yu Y, Ren F
Received 27 December 2019
Accepted for publication 1 March 2020
Published 31 March 2020 Volume 2020:16 Pages 859—869
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S243551
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Jun Chen
Purpose: Gut microbiota affects various physiological functions in the host and has crucial effects on the nervous system. There is increasing evidence of a correlation between gut microbiota and depression; however, the mechanisms underlying the regulation of depression-like behavior by gut microbiota remain unclear. In this study, we assessed the regulatory mechanism of gut microbiota on depression-like behavior in rats.
Methods: We transplanted fecal microbiota obtained from patients with depression and healthy individuals into germ-free (GF) rats (n=18) through fecal microbiota transplantation technology. Next, we assessed the affective behavior in the rats using the forced swimming test and a sucrose preference test. We used enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) to determine the hippocampal levels of 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), dopamine (DA), and noradrenaline (NE) and the serum levels of corticosterone (CORT), adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interferon-γ (IFN-γ), interleukin-6 (IL-6), interleukin-1 (IL-1), interleukin-1 (IL-4), and interleukin-1 (IL-10). The mitochondrial morphology of small intestinal epithelial cells was observed through transmission electron microscopy.
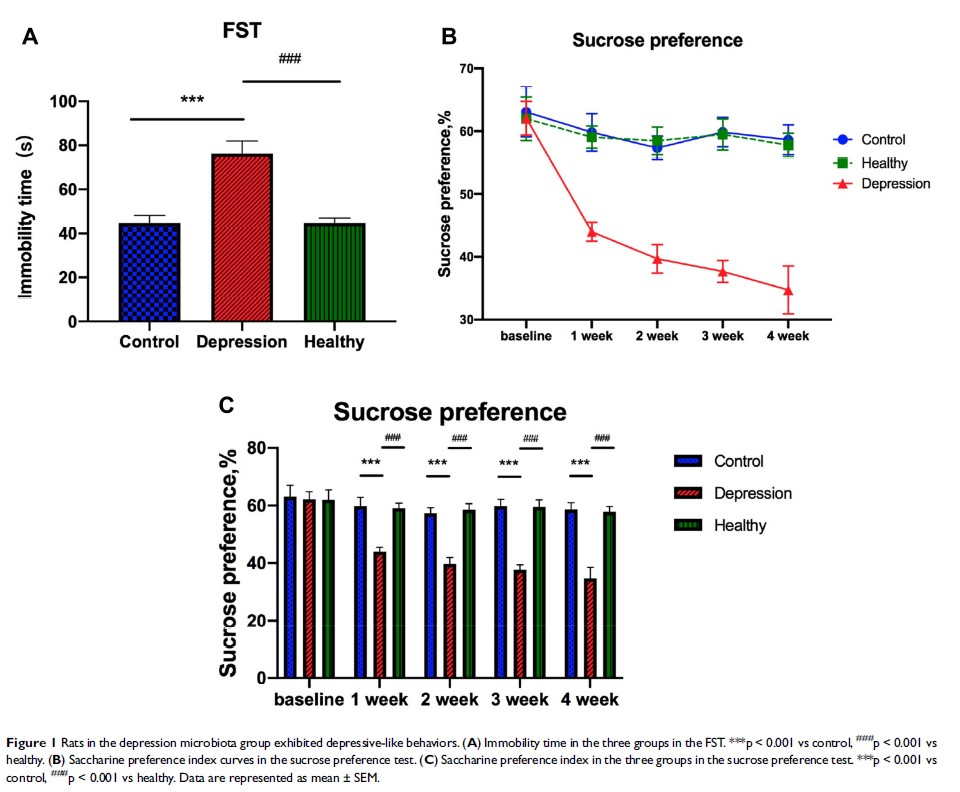
Results: Rats that received fecal microbiota from patients with depression (depression microbiota) exhibited depression-like behavior. They presented decreased levels of hippocampal neurotransmitters, serum CORT levels, and anti-inflammatory cytokine levels, as well as increased ACTH, CRH, and serum levels of multiple pro-inflammatory cytokines. Observation of the mitochondria ultrastructure showed damaged mitochondria in the intestinal epithelial cells, significant endoplasmic reticulum expansion, and border aggregation of nuclear chromatin.
Conclusion: Our findings suggested that the depression-like behaviors induced by the depression microbiota through the neuroendocrine-immune-mitochondrial pathway, which were associated with neuroendocrine disorders, inflammatory responses, and mitochondrial damage.
Keywords: gut microbiota, depression, neurotransmitter, HPA axis, immune, mitochondrial